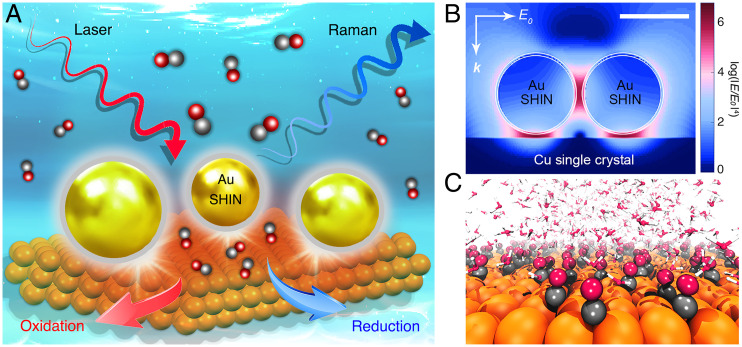
Fig. 1.
In situ electrochemical SHINERS and theoretical simulation for studying the CO redox at Cu surfaces. (A) Schematic illustration of the in situ EC-SHINERS technique used to study the electrochemical CO redox at Cu single-crystal surfaces in various electrolytes. (B) 3D-FDTD simulation of the field distribution within the coupling configuration between a Cu surface and a 2 × 2 array of Au@SiO2 SHINs (scale bar, 50 nm). E and E0 denote the localized electric field and the incident electric field, respectively; the Raman enhancement factor is proportional to the fourth power of the local field enhancement (|E/E0|4); k represents the wavevector of the incident light. (C) Schematic representation of an AIMD simulation model, where Cu, C, O, and H atoms are presented in orange, black, red, and white colors, respectively.