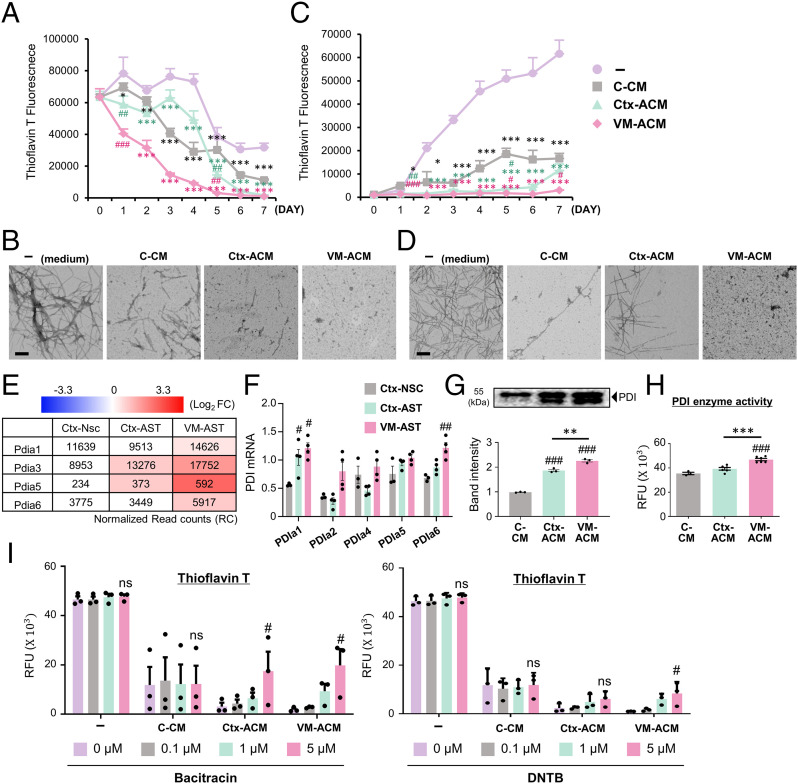
Fig. 3.
Extracellular α-syn disassembling and antiaggregation activities of astrocyte-derived paracrine molecules. (A and C) Time-course Thioflavin T assays to monitor disassembly of α-syn fibrils (A) and aggregate formation from α-syn monomers (C). Alpha-synuclein-PFFs (A) and monomers (C) were incubated at 37 °C with the VM-ACM, Ctx-ACM, C-CM, or medium (as a control). Thioflavin T assays were done at the time points of incubation indicated. (B and D) TEM images for the dissembled or aggregated α-syn at 7 (A and C) days after incubation. (Scale bars: 200 nm.) Significantly decreased from no CM (−) at *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, and ***P < 0.001 and C-CM at #P < 0.05, ##P < 0.01, and ###P < 0.001, n = 3 independent experiments, one-way ANOVA. (E–H) PDI mediates the ACM-mediated α-syn disassembly. (E and F) Messenger RNA expression of PDI isozymes detected by RNA-seq (accession no. GSE106216) (E) and real time-PCR (F) analyses. Expression in RNA-seq data is represented by the read count (RC) normalized using DESeq2 (v1.32) with the relative log expression (RLE) method (inside box) and Log2[Astrocyte/control Ctx-NSC] (color intensities). Significantly different from Ctx-NSC at #P < 0.05 and ##P < 0.01. (G and H) Secreted PDI protein levels and enzyme activities determined in the CMs. RFU, relative fluorescence units. Significantly different from C-CM at ###P < 0.001 and between the groups indicated at **P < 0.01 and ***P < 0.001, n = 3 to 6 of three independent experiments. (I) ACM-mediated α-syn disassembly activity blunted by the treatment of PDI inhibitors. α-syn PFFs were incubated with VM (Ctx)-ACM (or C-CM) in the presence or absence of the PDI inhibitors bacitracin and DTNB. Five days after incubation, α-syn disaggregation levels were determined by Thioflavin T assays. Significant differences from the inhibitor-untreated (0 μM) at #P < 0.05, n = 3 independent experiments, one-way ANOVA. ns, no significance.