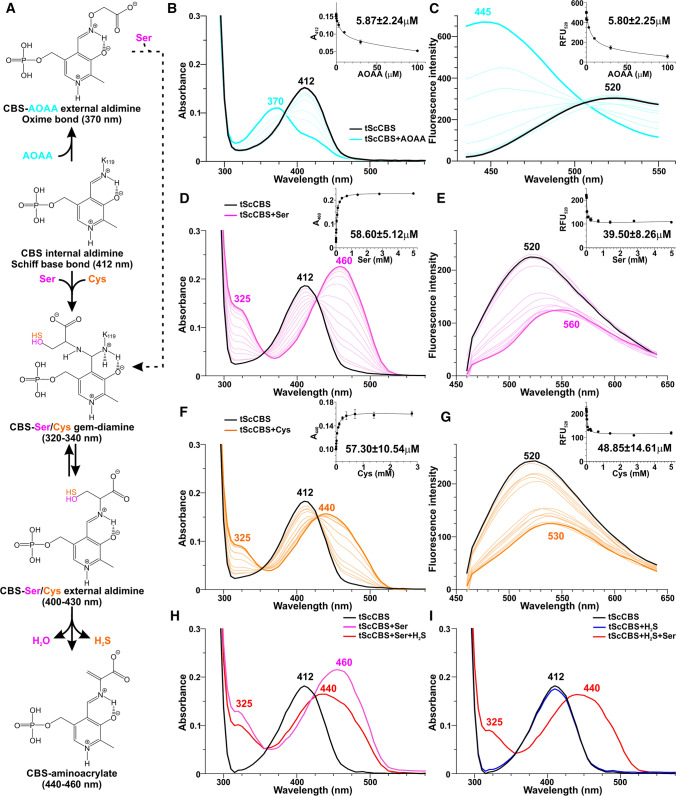
Fig. 1.
CBS reaction intermediates and UV–Vis absorption and fluorescence spectra of tScCBS in the presence of AOAA, Ser and Cys. A Proposed reaction mechanism of the first half of the CBS catalytic cycle with substrates (Ser, Cys) and inhibitor (AOAA) showing absorption maxima associated with the PLP-bound intermediates. B–G Changes in the UV–Vis absorption and fluorescence spectra of tScCBS (1 mg/mL in 50 mM Tris–HCl pH 8.5, 20 mM NaCl, 500 µM TCEP) upon addition of 0–100 µM AOAA (B–C), 0–5 mM Ser (D–E) and 0–5 mM Cys (F–G). Spectra were recorded after 3 min of incubation for each concentration. Fluorescence spectra were recorded between 435 and 650 nm after excitation at 410 nm. The insets show fittings of the spectral changes for the calculation of dissociation constants Kd from three independent measurements. H–I Changes in the UV–Vis absorption spectra of tScCBS upon addition of 1 mM Ser followed by addition of equimolar H2S donor (1 mM Na2S; H) and upon addition of 1 mM H2S followed by addition of equimolar 1 mM Ser (I)