Figure 3.
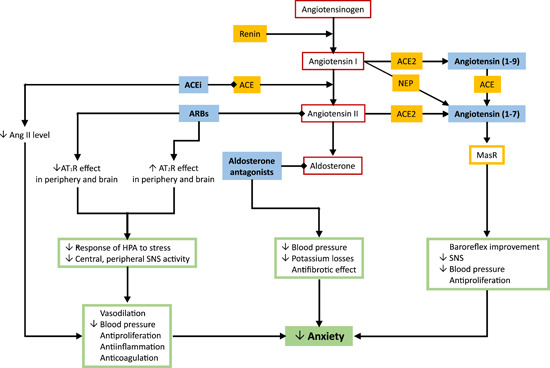
Modification of the renin‐angiotensin‐aldosterone system and its effect on anxiety.
The inhibition of the renin‐angiotensin system in the brain by angiotensin II type 1 receptor blockers (ARBs) or attenuating angiotensin II (Ang II) formation via angiotensin‐converting enzyme inhibitors (ACEi) exhibits neuroprotective effects and reduces the level of the stress response and anxiety. 103 , 104 , 109 , 192 The possible mechanisms underlying the anxiolytic effect of ARBs and ACEi include the upregulation of the Ang II type 2 receptor (AT2R) in the brain, and the enhancement of angiotensin (1–7) production acting on Mas receptors (MasR). 193 The stimulation of both AT2R by Ang II and MasR by angiotensin (1–7) is considered to protect the cardiovascular system via vasodilation and antiproliferative effects 194 , 195 while exerting anxiolytic effects. Similarly, aldosterone antagonists reduce hemodynamic burden, potassium losses, profibrotic effects, 196 , 197 and anxiety level. 132 , 133 ACE, angiotensin‐converting enzyme; AT1R, angiotensin II type 1 receptor; HPA, hypothalamic‐pituitary‐adrenal axis; NEP, neutral‐endopeptidase; SNS, sympathetic nervous system [Color figure can be viewed at wileyonlinelibrary.com]
