Fig. 2.
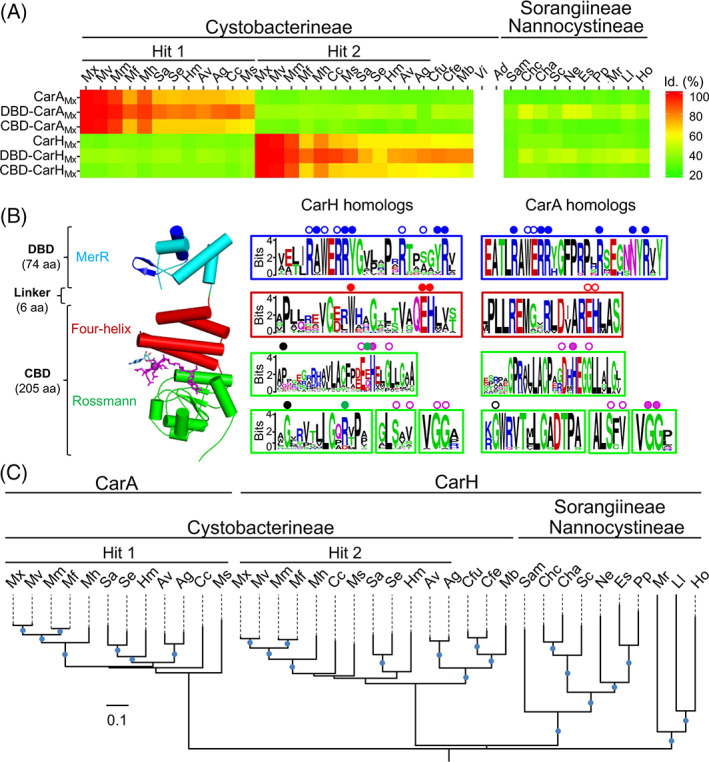
CarA and CarH homologues in Myxococcales.
A. Heat map of the sequence identities of myxobacterial CarH/A homologues relative to CarAMx, CarHMx and their DBDs or CBDs (see Table S1 for species abbreviations).
B. Left: Structure of the CarHTt protomer (PDB code: 5C8D) with its DBD (DNA recognition helix and wing in dark blue) and its CBD, with bound AdoCbl (sticks in magenta with upper axial Ado group in cyan). Right: Weblogos of myxobacterial CarH/A homologues alongside the corresponding subdomains in CarHTt. Dots indicate DNA contacts (blue), Wx9EH motif (red), lower axial B12‐binding motif (magenta), dimer contacts (green) and dimer‐dimer interface (black), based on the CarHTt and DBD‐CarAMx structures, with filled dots indicating residues tested by mutational analysis (Navarro‐Avilés et al., 2007; Jost et al., 2015b).
C. Maximum likelihood phylogeny (blue dots >80% bootstrap values) for myxobacterial CarH and CarA homologues.
