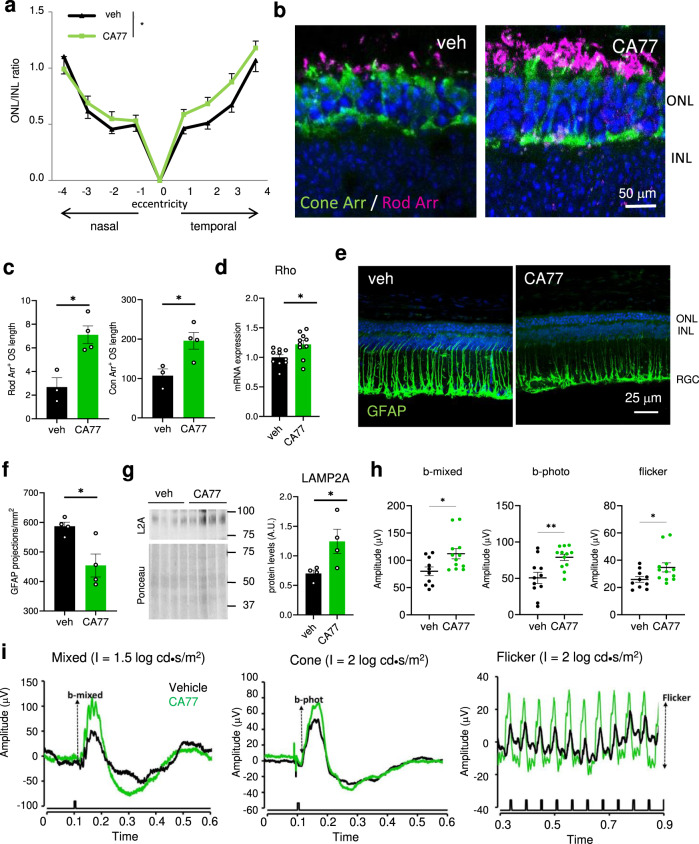
Fig. 6. CA compounds prevent rd10 retinas degeneration.
a Ratio of the thickness of the outer nuclear layer (ONL) and inner nuclear layer (INL) in retinas of rd10 mice treated from P18 to P25 with daily i.p. injection of the vehicle only or 40 mg/kg bw of CA77. n = 8 (vehicle) and 9 (CA treated), from 3 independent experiments. b Cone (green) and rod (magenta) arrestin markers in temporal central retina of rd10 mice treated as in a. Nuclei are highlighted with DAPI. c Quantification of outer segment (OS) length of the rods (left) and number of cones (right) measured in the whole retina with the markers used in b. n = 4 areas per animal, 4 mice per condition. d mRNA levels of rho in the same animals used in a. n = 10. e, f Representative image of the immunostaining for GFAP in the same retinas (e) and corresponding quantification of the GFAP projections (f). n = 4. g Immunoblot for the indicated proteins in retinas of mice treated as in a. 4 different mice are shown. Right: Densitometric quantification of L2A in n = 4 different mice. Values are expressed as arbitrary units. h, i Electroretinogram wave amplitudes at P33 from rd10 mice injected with CA77 or vehicle as in a (h) measured as shown in the traces (i). n = 10 veh and 12 CA77. Individual values and mean + s.e.m. are shown. Two-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni’s multiple comparisons post-hoc test was used in a, and unpaired two-tailed t test in all others. *p < 0.05 and **p < 0.01. Uncropped blots are in Supplementary Fig. 10. Source data and exact p values are provided as a Source Data file.