Figure 4.
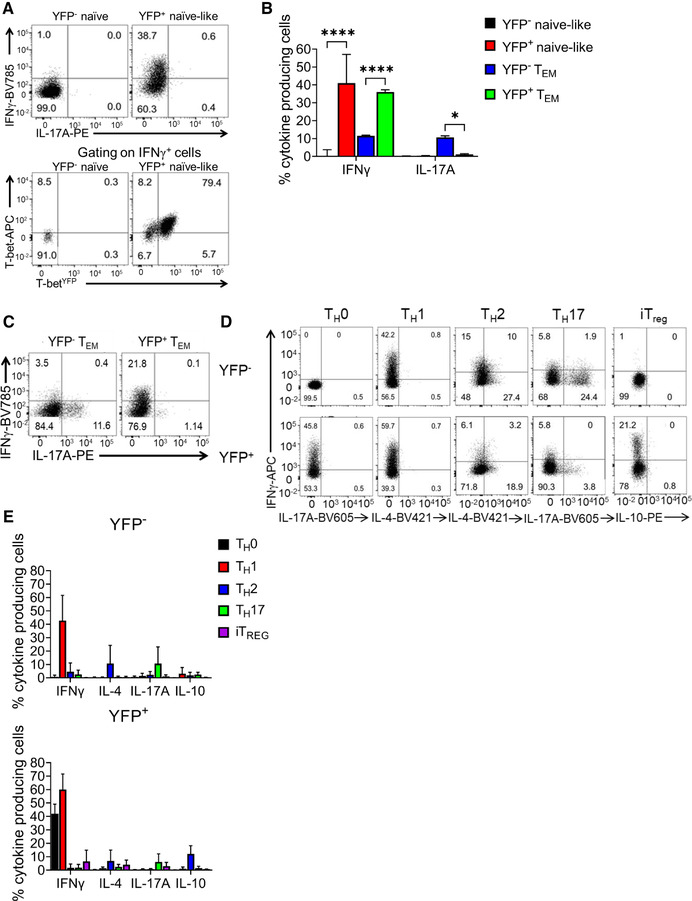
YFP+ naïve‐like CD4+ T cells resist polarization toward other CD4+ T‐cell lineages. (A) Representative flow plots from three independent experiments (each comprising three replicates) showing cytokine expression (top) or T‐bet and YFP expression (bottom) in YFP– and YFP+ naïve‐like (CD62L+ CD44–) CD4+ T cells after in vitro activation with anti‐CD3/CD28 and culture with IL‐2. (B) Percentage of cultured YFP– and YFP+ naïve‐like (CD62L+ CD44–) CD4+ T cells and TEM (CD62L–CD44+) producing IFN‐γ or IL‐17A after activation with anti‐CD3/CD28 and culture with IL‐2 (median with range shown, n = 9), *p < 0.05, ****p < 0.0001 (Two‐way ANOVA). (C) Representative flow plots from three independent experiments (each comprising three replicates) showing cytokine expression from in vitro cultured YFP– and YFP+ TEM after activation with anti‐CD3/CD28 and culture with IL‐2. (D) Representative flow plots from three independent experiments (each comprising two replicates) showing cytokine expression in naïve‐like (CD62L+ CD44–) YFP– and YFP+ CD4+ T cells after activation with anti‐CD3/CD28 and polarization in TH0, TH1, TH2 TH17 and iTreg conditions in vitro. (E) Proportion of naïve‐like (CD62L+ CD44–) YFP– and YFP+ CD4+ T cells producing cytokines after activation with anti‐CD3/CD28 and polarization in TH1, TH2 TH17 and iTreg conditions in vitro (median with range shown, n = 6).
