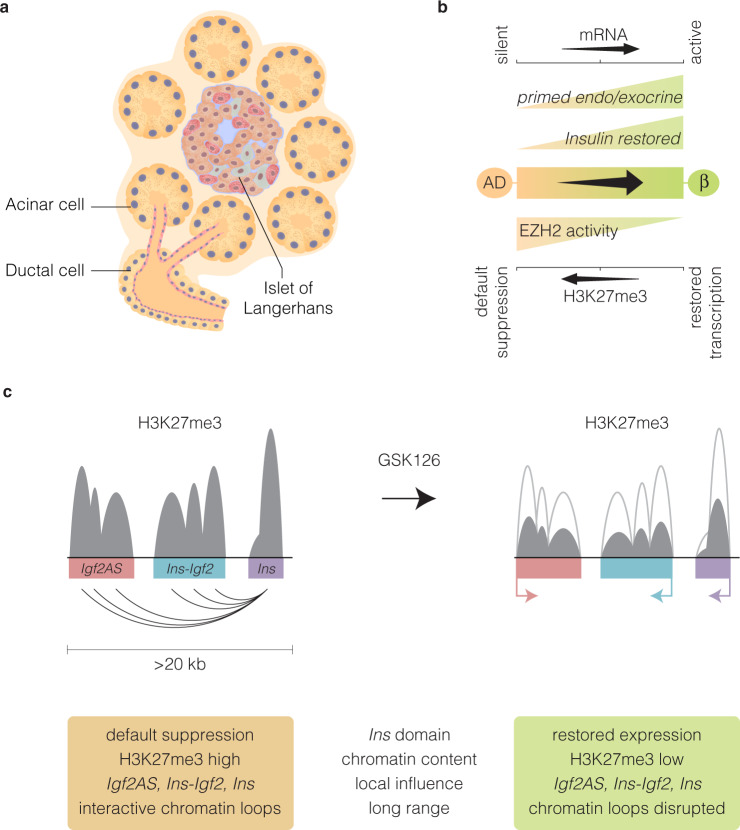
Fig. 6.
Schematic representation of pancreatic progenitor differentiation and the refractory influence of H3K27me3 content on the insulin chromatin domain in human exocrine cells. a Organisation of the human endocrine and exocrine pancreas showing the main pancreatic ductal tree connecting the acinar bundle. b The inability to influence transcriptional expression in the exocrine and endocrine pancreas is in accordance with default transcriptional suppression mediated by EZH2 dependent H3K27me3. Conversion of default repression state in the acinar and ductal (AD) cells is influenced by pharmacological inhibition of EZH2 by GSK126 to prime β-cell lineage regeneration and restore insulin expression. c Proposed model of the Ins chromatin domain in pancreatic cells. Default transcriptional suppression is characterised with H3K27me3 rich regions can influence chromatin conformation, and suppress the expression of Ins, Igf2AS and Ins-Igf2 genes postulated by long-distance chromatinised-looping. We propose GSK126 attenuates EZH2 activity to influence local H3K27me3 chromatin content and long-distance interactions that function on the Ins chromatin domain and gene expression