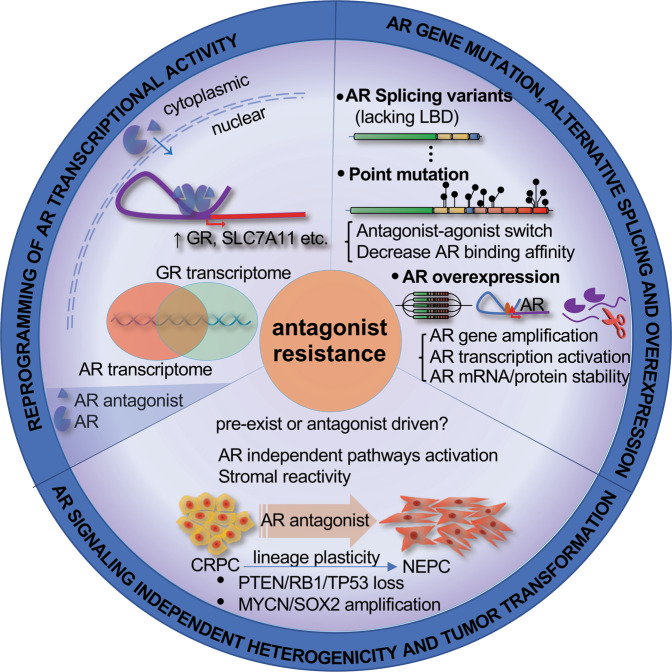
Fig. 4. Mechanisms of resistance to androgen receptor inhibitors in prostate cancer.
The partial agonist role of second-generation AR antagonists induces the expression of cancer-related genes including GR. GR in turn regulates the expression of a set of genes that overlaps with AR downstream pathways. AR alterations can include alternative splicing, point mutation and overexpression. Other AR signaling-independent mechanisms such as PTEN/TP53/RB1 loss of function and MYCN/SOC2 activation can mediate CRPC progression and contribute to AR antagonist resistance in CRPC.