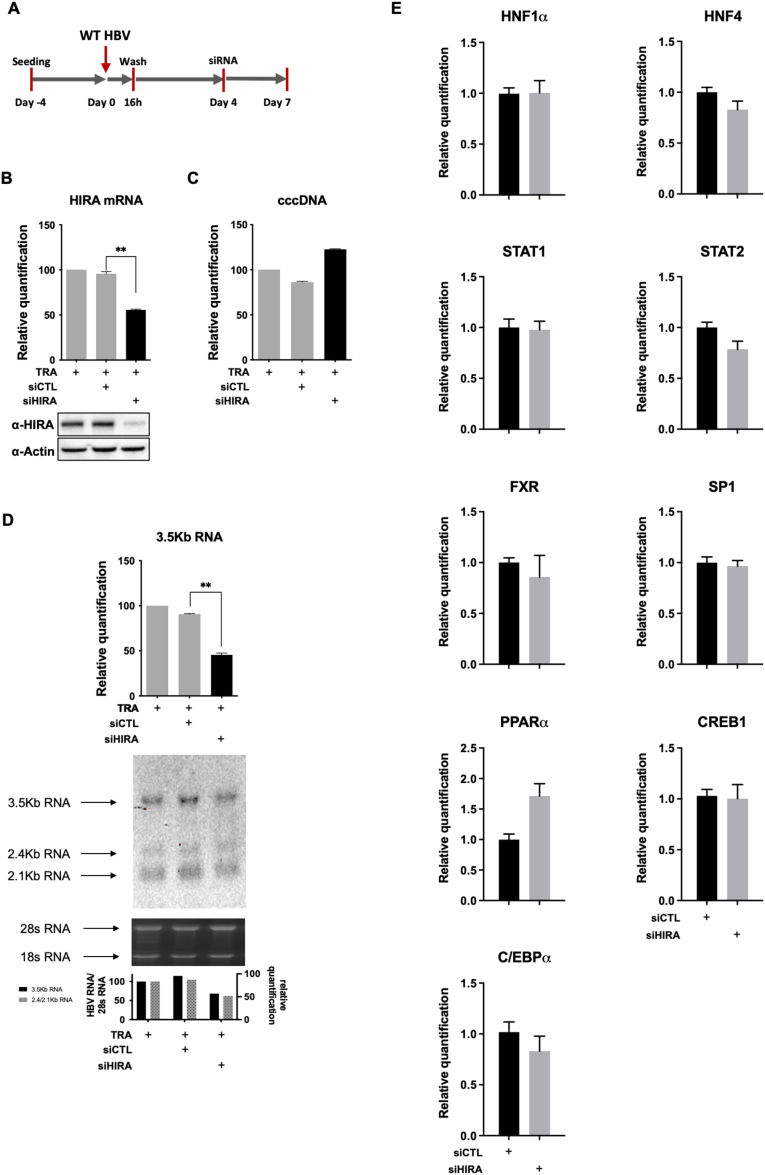
Figure 11.
HIRA is required for the maintenance of cccDNA transcriptional activity. (A) Experimental timeline for HIRA knock-down after HBV infection. HepG2hNTCP cells were infected for 16 hours and then extensively washed and transfected with siHIRA or siCTL at 4 dpi. Cells were harvested for analysis at 7 dpi. (B) HIRA messenger RNA (mRNA) and protein expression after siRNA transfection was determined by real-time qPCR and Western blot. β-actin served as Western blot loading control. (C) cccDNA and (D) 3.5-kb RNA amount was measured by qPCR and Northern blot at 7 dpi. cccDNA quantification was normalized over β-globin quantity, while relative 3.5-kb RNA amount was normalized over the housekeeping gene GUSb expression. (E) HepG2hNTCP cells were transfected with siRNA against HIRA according to the timeline shown in Figure 2B and inoculated for 16 hours with HBV at 250 viral genome equivalents/cell. The cells were harvested for analysis at 7 dpi. mRNA levels of hepatocyte nuclear factor-1α (HNF1α), hepatocyte nuclear factor-4α (HNF4α), signal transducer and activator of transcription 1 and 2 (STAT1, STAT2), nuclear receptor farnesoid X (FXR), specificity protein 1 (SP1), peroxisome proliferator activated receptor α (PPARα), CAMP responsive element binding protein 1 (CREB1), and CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein α (C/EBPα) were quantified by real-time qPCR assay and expressed as a percentage of TRA-treated cells after normalization over GUSb housekeeping gene expression. Data represent the means ± SEM of at least 3 independent experiments. Graphs represent the means ± SEM of at least 3 independent experiments. The 2-tailed P value was calculated for a risk threshold of .05 using the 2/K sample permutation test with Monte Carlo resampling approximation. ∗∗P < .01.