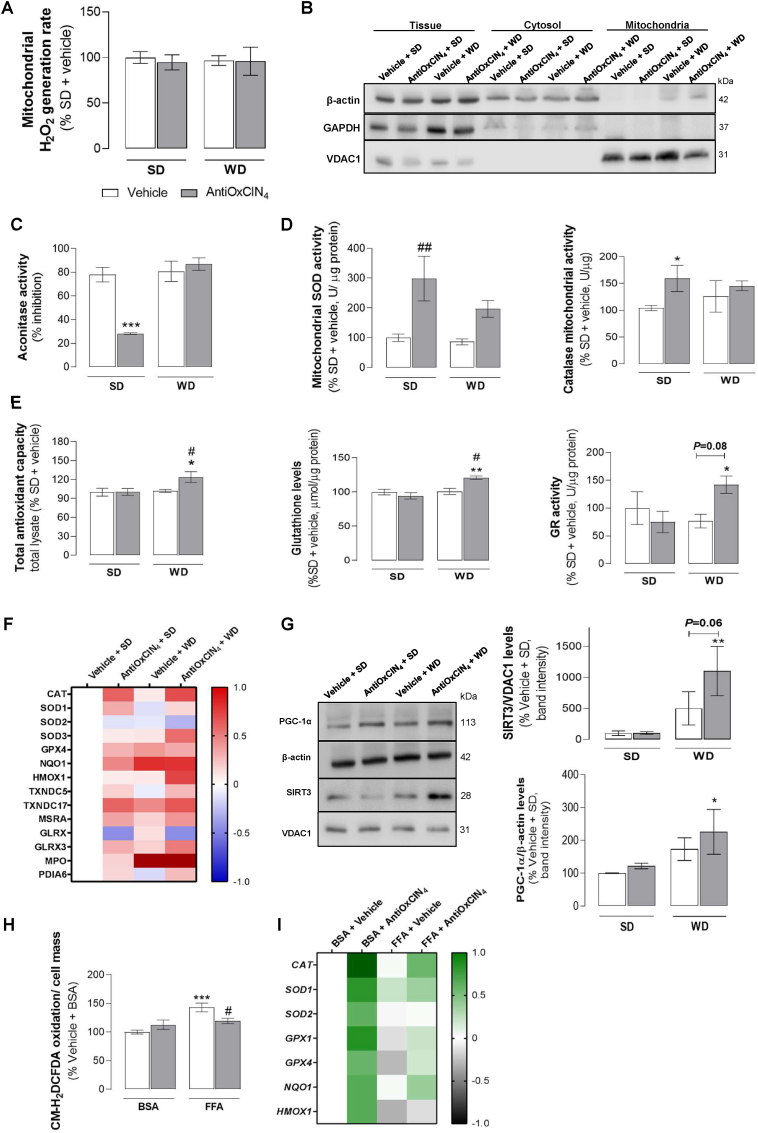
Fig. 5.
Effects of AntiOxCIN4on oxidative stress hallmarks and anti-oxidant defenses of a WD-fed mice with NAFL phenotype and FFAs-treated human HepG2 cells. (A) H2O2 production rate in isolated liver mitochondria from WD-fed mice in the absence/presence of AntiOxCIN4 (2.5 mg/day/animal). (B) Typical Western blot results showing the purity of cytosolic and mitochondrial fractions by using β-actin, GAPDH and VDAC1 levels. (C) Aconitase activity inhibition, superoxide dismutases (SODs) and catalase activities in isolated liver mitochondrial fraction from WD-fed mice in the absence/presence of AntiOxCIN4 (2.5 mg/day/animal). (D) Total anti-oxidant capacity, glutathione reductase (GR) activity, and glutathione (GSH) levels in whole liver homogenate from WD-fed mice in the absence/presence of AntiOxCIN4 (2.5 mg/day/animal). (E) MS-proteomic analysis of hepatic antioxidant-related enzymes levels in WD-fed mice in the absence/presence of AntiOxCIN4 (2.5 mg/day/animal). The blue color represents a decrease, while the red color represents an increase in protein levels. (F) Typical Western blot result of whole-liver homogenates depicting the cytosolic protein levels of PGC-1α and mitochondrial protein levels of SIRT3 from WD-fed mice in the absence/presence of AntiOxCIN4 (2.5 mg/day/animal). These blots were inverted and contrast-optimized for visualization purposes. Quantification of the bands was performed using the original blots. Quantification of protein levels in multiple experiments were normalized to β-actin (cytosol) or VDAC (mitochondria) levels. (G) Cellular reactive oxygen species (ROS) on HepG2 cells treated with vehicle (BSA) or FFA (24 h, 250 μM) in the absence/presence of AntiOxCIN4 (48 h, 100 μM). (H) mRNA transcript levels of antioxidant-related genes (CAT, SOD1, SOD2, GPX1, GPX4, NQO1 and HMOX1) in cells treated with vehicle (BSA) or FFA (24 h, 250 μM) in the absence/presence of AntiOxCIN4 (48 h, 100 μM) (right). The grey color represents a decrease, while the green color represents an increase of gene expression levels. Data are expressed as the mean ± SEM (N = 5 per cage for the in vivo study and N = 4 for the HepG2 studies) and the results were normalized to the control condition (set as 100%). Statistically significant compared using two-way ANOVA followed by Fisher's LSD test for multiple comparisons (*P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.0005 vs SD or Vehicle + BSA); (#P < 0.05, ##P < 0.01 vs WD or Vehicle + FFAs).