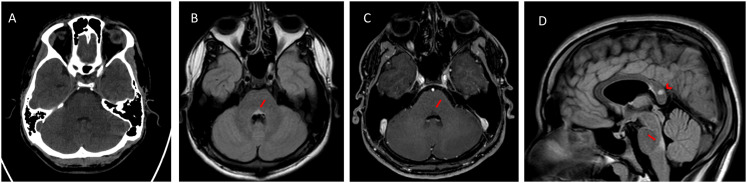
Figure 2.
A) Axial computed tomography on hospital admission, at the level of the posterior pontine tegmentum lesion, showing unremarkable findings. B) Axial FLAIR image showing a hyperintense lesion, which was responsible for horizontal gaze palsy. C) Axial T1-weighted image obtained after gadolinium administration showing no lesion enhancement. D) Sagittal FLAIR image showing the vertical extent of the lesion in the posterior pontine tegmentum (arrow); another MS lesion in the splenium of the corpus callosum was noted as an incidental finding (arrowhead).