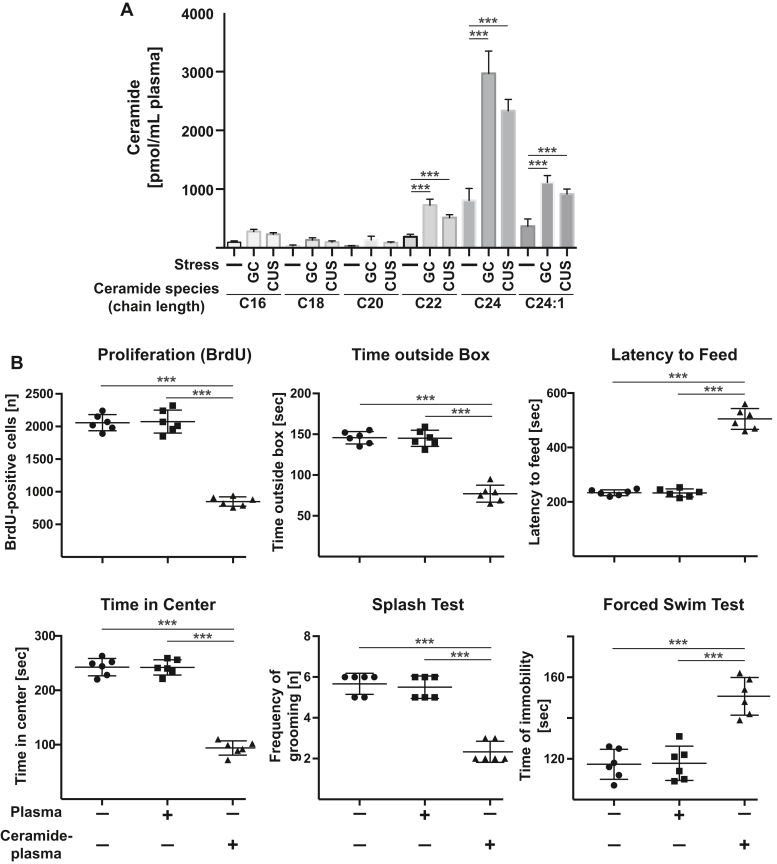
Figure 4.
Intravenous injection of ceramide-loaded blood plasma induces symptoms of major depressive disorder. A, ceramide species in the blood plasma of mice that were left untreated or stressed with glucocorticosterone (GC) or chronic unpredictable stress (CUS) were determined by mass spectrometry. Shown are the mean ± SD of six independent samples (same as in Fig. 1), ANOVA followed by Sidak´s multiple comparison test. Compared were the corresponding values of ceramide species after glucocorticosterone or CUS with those of untreated animals. B, plasma was isolated from the blood of untreated wildtype mice, loaded with a total of 5 nmol ceramide at a ratio of 5.2% C16 : 2.4% C18 : 2.5% C20 : 13.6% C22 : 55.5% C24 : 20.8% C24:1 ceramides, and injected intravenously (i.v.) into wildtype mice. Neurogenesis and behavioral changes were measured as readout for the induction of MDD by i.v. ceramide loaded plasma. Presented are the mean ± SD from each six mice. ∗∗∗p < 0.001, ANOVA and post hoc Tukey test.