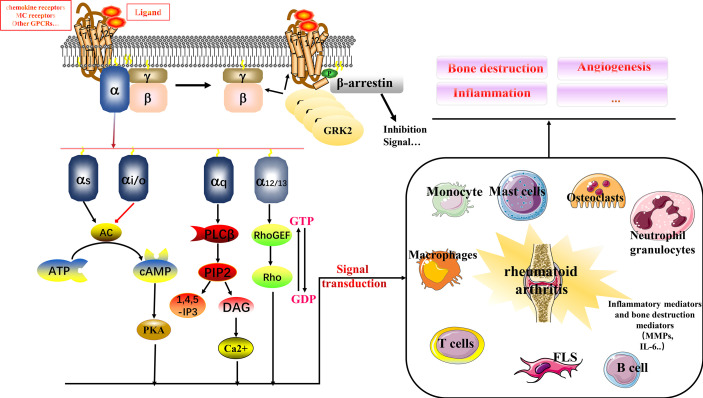
Figure 1.
Relationship between multiple GPCRs and RA. GPCRs signal through the αβγ subunit of heterotrimeric G proteins. In response to ligand signals, GTP binds to the Gα subunit, and Gβγ dissociates to form a dimer for downstream signaling, binding to biological mediators. GRK2 is a kinase that phosphorylates activated GPCRs, making them a high-affinity substrate for the binding of the uncoupling protein arrestin. Arrestin binding abolishes (“arrests”) G protein-mediated signaling. The binding of GRK2 to Gβγ recruits cytosolic GRK2 to the plasma membrane, where the activated receptor is located. This is its primary function. It can also inhibit Gβγ-mediated signaling by sequestering Gβγ, which is a secondary effect. GPCRs interact with immune cells in RA to influence multiple mechanisms including bone destruction, inflammation, and angiogenesis.