Figure 2.
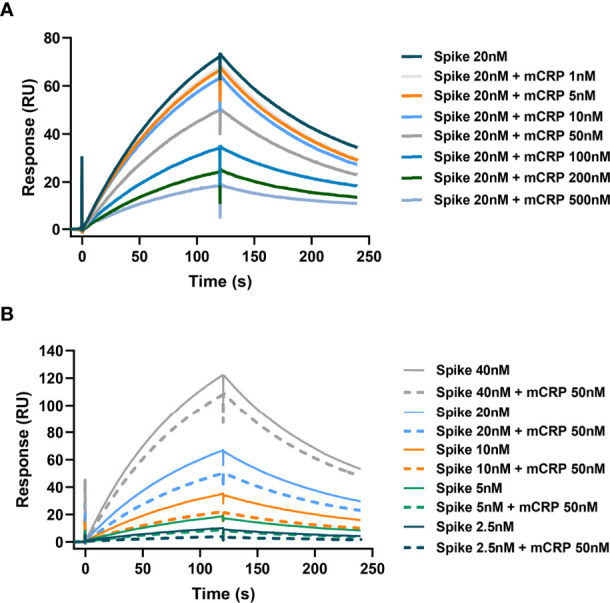
mCRP competitively inhibits the binding of the spike RBD to ACE2. (A) mCRP competes for the binding of spike RBD to ACE2 in a concentration-dependent manner. In the surface plasmon resonance (SPR) binding assay, different concentrations of mCRP were added to compete for the binding of the spike RBD to ACE2. Results showed that mCRP competed for the binding of the spike RBD to ACE2 in a concentration-dependent manner. (B) A fixed concentration of mCRP competes with the binding of different concentrations of the spike RBD to ACE2. For detecting the binding of different concentrations of the spike RBD to ACE2 (solid line), a fixed concentration of mCRP was added to compete for binding (dotted line), and mCRP competitively inhibited the binding of the spike RBD to ACE2.
