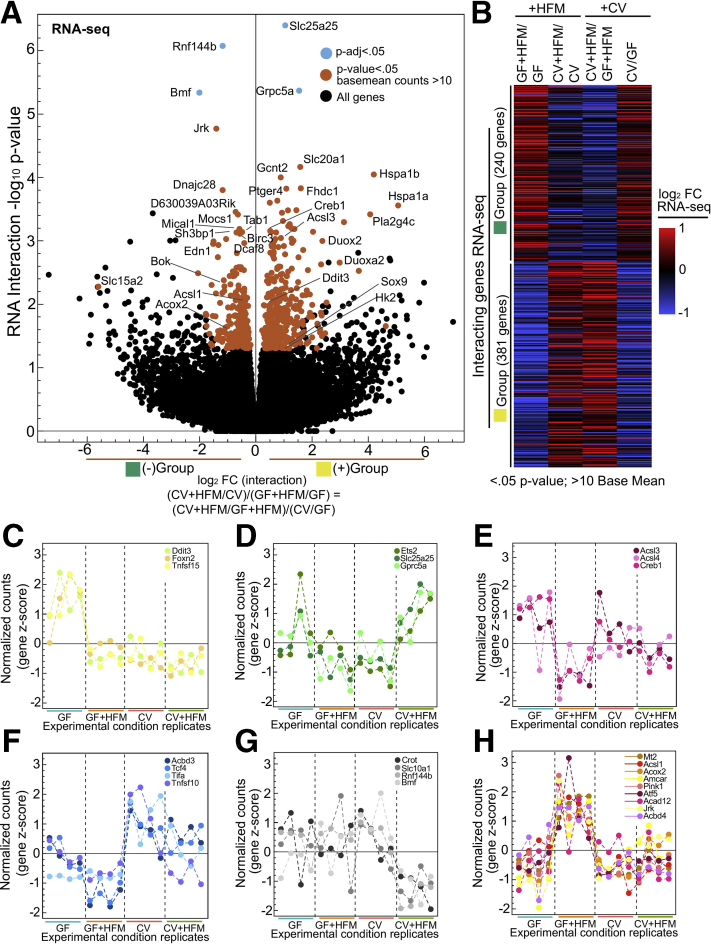
Figure 3.
Characterizing putative transcriptional interaction genes. (A) Volcano plot showing interaction log2 fold change versus –log10P value for typical (P adjusted <.05; blue) and lenient (P value <.05, >10 base mean counts; red) cutoffs identifies genes with greatest potential for interaction. In effect, the interaction log2 fold change represents the log2 ratio of (CV+HFM/CV)/(GF+HFM/GF) or (CV+HFM/GF+HFM)/(CV/GF), which are equivalent because these comparisons contain the same 4 conditions. Because negative (–, green) and positive (+, yellow) interactions are representative of the directionality of the fold change but not necessarily the nature of the interactions, these groups are also colored to help illustrate that property. (B) Heatmap of log2 FC for each comparison for interaction genes broken into the green and yellow groups. (C–H) RNA-seq z-scored normalized counts for example interacting genes, with each panel showing a different expression pattern.