FIGURE 2.
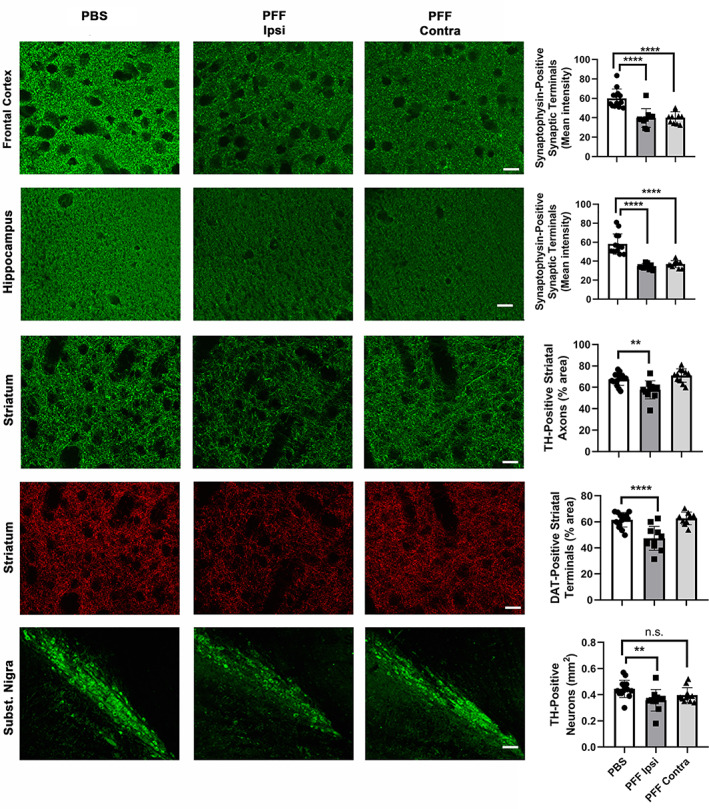
Striatal injection of murine α‐syn PFFs induced neurodegeneration in various brain regions. Mice were euthanized 90 dpi. In the frontal cortex and the hippocampus, a significant bilateral loss of synaptophysin‐positive presynaptic terminals was observed (first two rows). In the striatum, a significant ispilateral loss of TH‐positive axonal fibers and DAT‐positive synaptic terminals was observed (3rd and 4th row). In the SN, a significant loss of TH‐positive neurons was observed only ipsilaterally. For group comparisons and graphing, ipsilateral PBS measures were combined contralateral PBS measures, since they were similar. Pictures show the ipsilateral side of PBS‐injected mice. ****p < .0001, **p < .01, compared to PBS controls by Dunnett's post hoc; n = 10–11/group; graphs are mixed scattergrams/bar diagrams, where points represent the individual values for each animal, and bars represent the means +/− SD; 95% confidence intervals of differences: Frontal cortex – PBS versus PFF ipsi: 11.6 to 28.7, PBS versus PFF contra: 11.42 to 28.52; hippocampus – PBS versus PFF ipsi: 16.2 to 30.5, PBS versus PFF contra: 13.9 to 28.3; striatum (TH) – PBS versus PFF ipsi: 3.56 to 16.3, PBS versus PFF contra: −9.8 to 2.9; striatum (DAT) – PBS versus PFF ipsi: 7.8 to 20.6; PBS versus PFF contra: −7.8 to 5.7; SN (TH) – PBS versus PFF ipsi: 0.002 to 0.152, PBS versus PFF contra: −0.017 to 0.112). Scale bars: 18 μm (for frontal cortical and hippocampal synaptophysin panels), 22.5 μm (for striatal TH and DAT panels), 80 μm (for Subst. Nigra panels)
