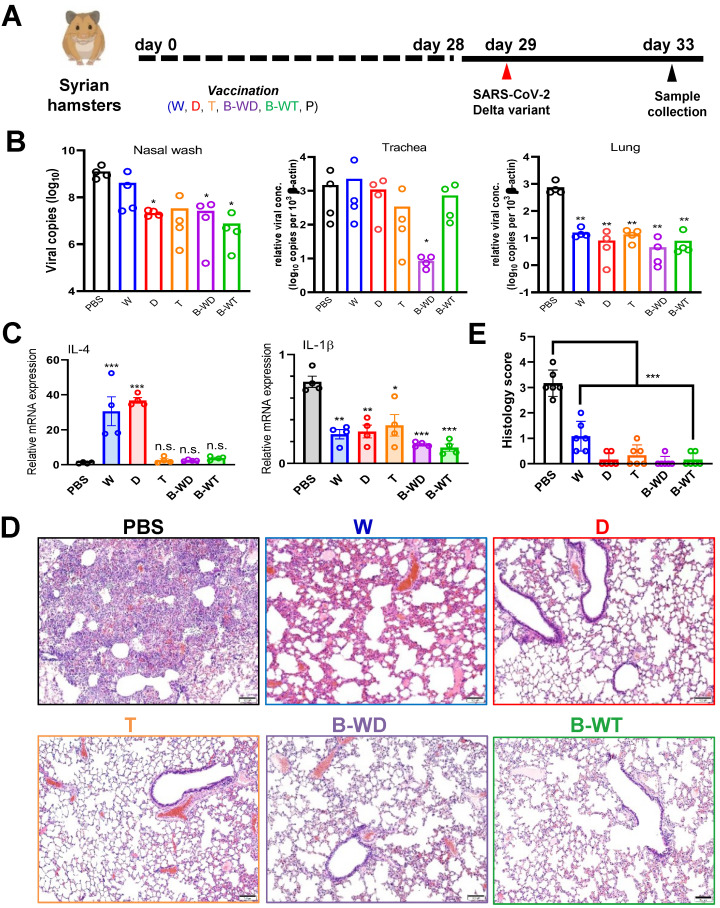
Figure 4.
Vaccination with the indicated inactivated viruses confers protection to infection of hamster lung with SARS-CoV-2 Delta strain. (A) Virus challenge scheme. Vaccinated hamsters were intranasally inoculated with 105 PFU (in 50μl) of SARS-CoV-2 Delta variant. At 4 dpi (i.e., 33 days after vaccination), viral titers in hamster nasal wash, tracheal and lung samples were quantitated by RT-qPCR (B). (C) Cytokine gene expression in Delta variant-infected hamsters. Transcripts of representative chemokines and cytokines in the lung tissue homogenates of the indicated groups were quantitated by RT-qPCR. Results are shown as means ± SEM. Statistical analysis was performed by Student's t test and comparison was made to the PBS group (n.s.: not significant; *: P < 0.05; **: P < 0.01; ***: P < 0.001). (D) Impact of vaccination on histopathological changes in lungs of SARS-CoV-2 Delta variant-infected hamsters. Lung histopathological changes of each vaccinated hamster group at 4 dpi. Representative lung tissue sections were stained with hematoxylin and eosin. Bar, 100 μm. (E) Pathological changes in Delta-infected lungs from indicated vaccinated groups, scored as described in Methods (**: P < 0.01).