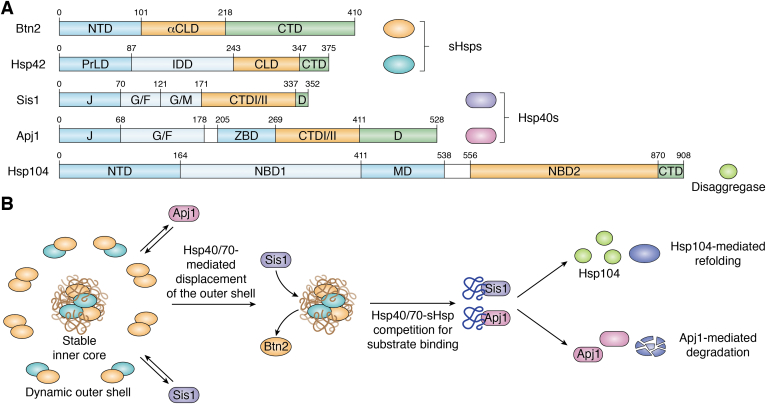
Figure 2.
Chaperones at INQ.A, domain architecture of five chaperones that have been found at INQ. NTD = N-terminal domain; αCLD = alpha-crystallin–like domain; CTD = C-terminal domain; PrLD = Prion-like domain; IDD = intrinsically disordered domain; CLD = alpha crystallin domain; J = J-domain; G/F = glycine/phenylalanine rich domain; G/M = glycine/methionine rich domain; D = dimerization domain; ZBD = zinc-binding domain; NBD1/2 = nucleotide-binding domain 1 or 2; MD = middle domain. B, competition-based model between Hsp40/70-sHsp proteins decides INQ substrate fate. The model shows that an exchangeable shell of sHsps enables access of Hsp40/70 chaperones to non-native substrates ready to enter the refolding or degradation pathway. Figure was created with BioRender.