FIGURE 2.
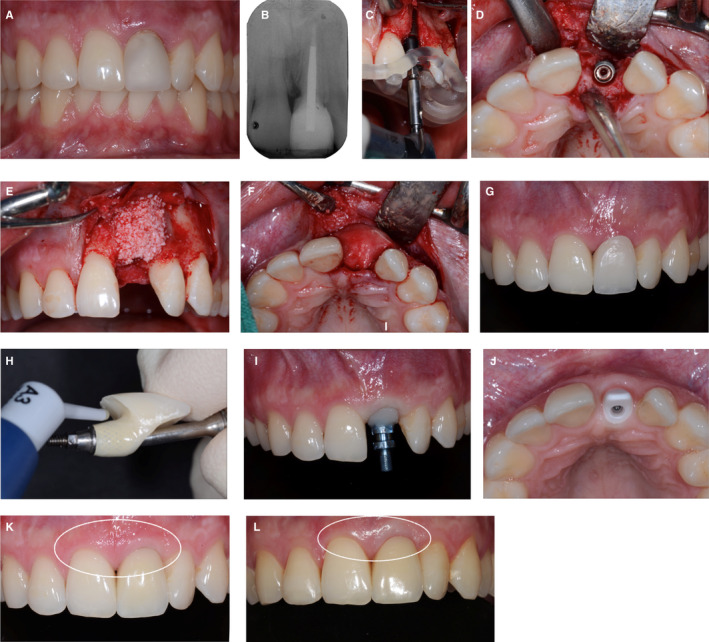
A and B, Clinical situation of a 24‐year‐old male patient with a failing left central incisor. The tooth lost vitality following an accident during the childhood of this patient. C and D, Replacement of the incisor by means of a bone‐level type of implant, with the aid of a guided surgery approach. E and F, Simultaneous guided bone regeneration to augment the volume of the ridge surrounding the implant with a xenograft and a collagen membrane (BioOss granules, BioGide membrane; Geistlich Pharma, Wolhusen, Switzerland). Submerged healing of the implant. G and H, Status after second stage surgery and insertion of a screw‐retained fixed implant provisional. Conditioning of the peri‐implant mucosa in a stepwise approach by application of a light‐curing resin (Tetric Flow, Ivoclar Vivadent, Schaan, Liechtenstein) to the submucosal part of the implant provisional, in order to receive a natural emergence profile of the implant restoration. I, Fixture‐level implant impression with a customized implant impression copying the submucosal part of the conditioned implant provisional for the final restoration. J, Fabrication and try‐in of the white zirconia abutment, foreseen for the support of a laboratory‐cemented glass‐ceramic crown, screw‐retained at delivery. K, Paleish, whitish discoloration of the peri‐implant mucosa at the implant in the left central incisor region. Status 30 min after insertion. L, Four‐year recall examination of the implant crown; note the still visible paleish appearance of the peri‐implant soft tissues, caused by the white zirconia substructure
