Fig. 2.
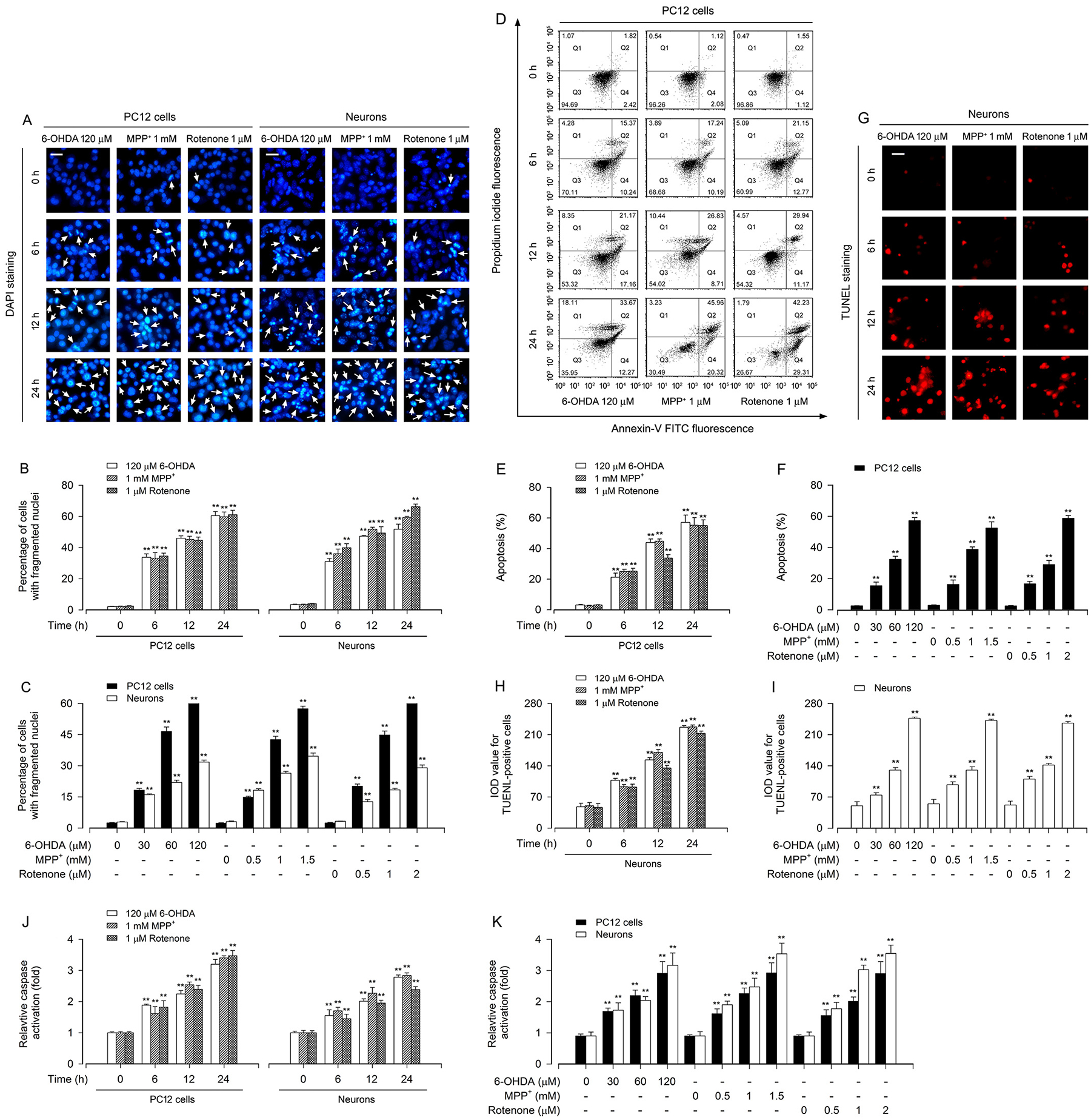
Apoptosis is triggered in PD toxins-induced neuronal cells. PC12 cells and primary neurons were treated with 6-OHDA (30, 60 and/or 120 μM), MPP+ (0.5, 1 and/or 1.5 mM) or rotenone (0.5, 1 and/or 2 μM) for 6, 12 and/or 24 h. A Apoptotic cells were evaluated by nuclear fragmentation and condensation (arrows) using DAPI staining. Scale bar: 20 μm. B and C The percentage of cells with fragmented nuclei was quantified. D The percentages of necrotic (Q1), late apoptotic (Q2), live (Q3) and early apoptotic (Q4) cells were determined by FACS using annexin-V-FITC/PI staining. The results from a representative experiment in PC12 cells are shown. E and F Quantitative analysis of apoptotic cells by FACS assay. G Apoptotic cells were evaluated by in situ detection of fragmented DNA (in red) using TUNEL staining. Scale bar: 20 μm. H and I IOD values of TUNEL-positive cells with the fluorescence staining were quantified. J and K Caspase-3/7 activities were detected using Caspase-3/7 Assay Kit. Results were presented as mean ± SEM, n = 5. **P < 0.01, difference with control group.
