Fig. 8.
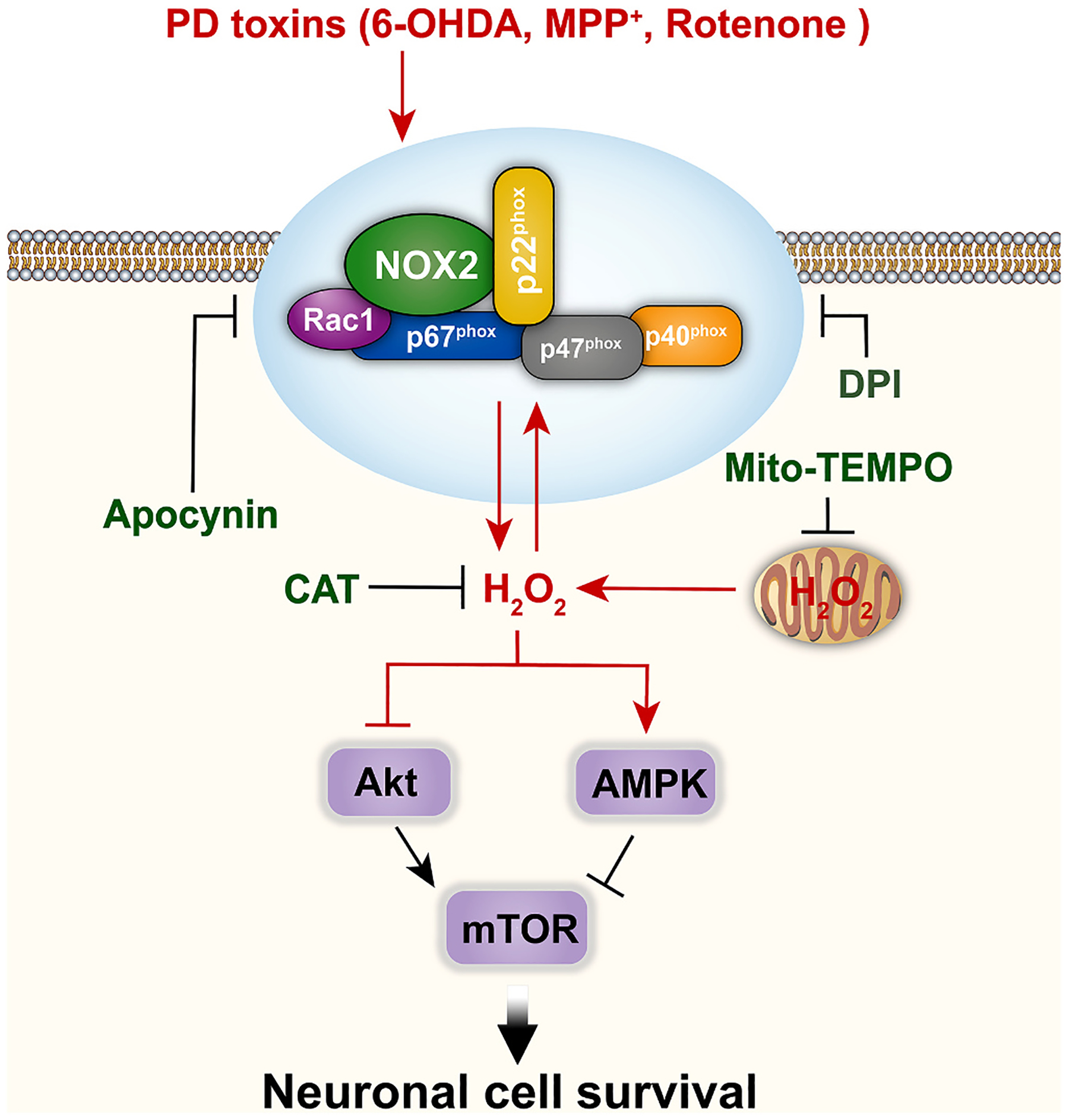
A schematic model of how PD toxins (6-OHDA, MPP+ or rotenone) induce NOX2-derived H2O2 leading to neuronal apoptosis. PD toxins upregulate the expression of NOX2 and its regulatory proteins, and thus evoke intracellular H2O2 and concomitant mitochondrial H2O2. This results in activation of AMPK and inactivation of Akt, convergently inhibiting the mTOR pathway contributing to apoptosis in neuronal cells.
