Figure 1.
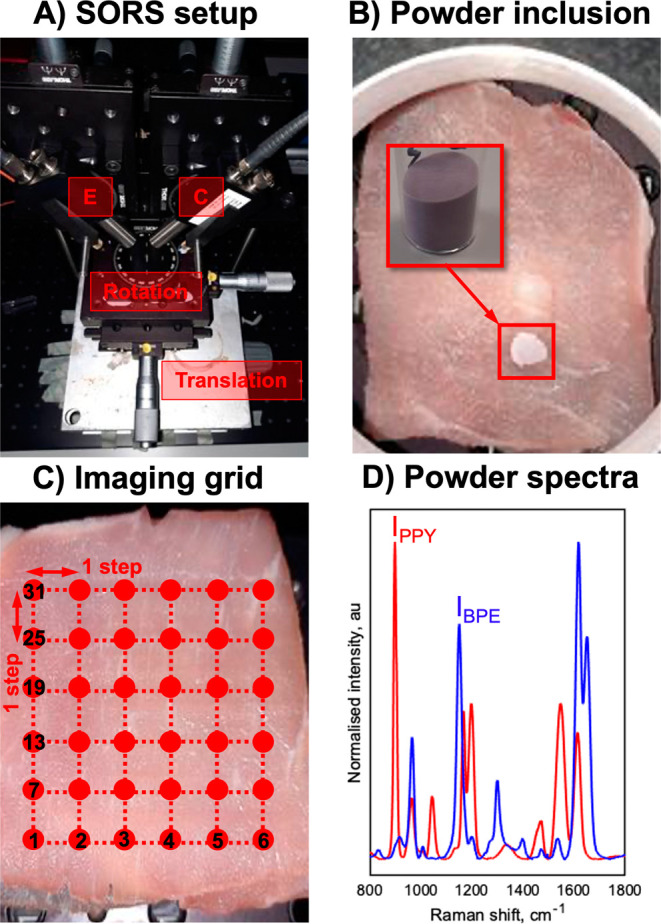
(A) SESORS experiments were conducted on an in-house-built SORS system with a point-based collection geometry, i.e., with individual excitation (E) and collection (C) probes, developed by Asiala et al. based on the design of Shand and co-workers.21,23 (B) Templates for SESORS experiments were prepared by mixing the silica powder with silica-coated SERS-active NPs. The NP powders were then added to a section of the porcine tissue and then covered with further tissue sections. (C) Hypothetical SESORS imaging regime illustrated using a square grid, where each vertex on the grid represents a pixel where the tissue surface is excited by the laser. In the regime illustrated, the grid represents a 36-pixel (6 × 6) image. (D) Truncated, baselined, and normalized SERS spectra of PPY (red) and BPE (blue) powder-based imaging templates developed for this study. Spectra were collected for 0.1 s using a 785 nm, 400 mW laser.
