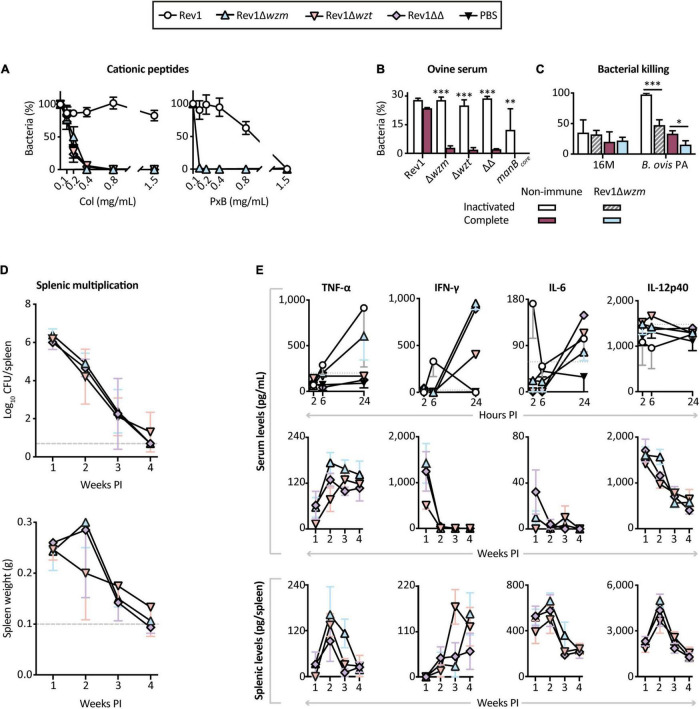
FIGURE 5.
Rev1Δwzm is highly attenuated and triggers a stronger adaptive immune response than Rev1Δwzt or Rev1ΔwzmΔwzt in the BALB/c mice. Susceptibility is shown for: (A) Polymyxin B (PxB) or colistin (Col), as models of cationic bactericidal peptides of the innate immune system (mean ± SD; n = 2); and (B) complement-mediated killing by conventional non-immune ovine serum, either complete or heat inactivated (mean ± SD; n = 2). (C) Bacterial killing activity of sera from sheep immunized with Rev1Δwzm against B. melitensis 16M and B. ovis PA (BoPA) virulent strains (mean ± SD; n = 4). (D) Kinetics of spleen infections and weights (mean ± SD; n = 3 at 1 and 4 weeks PI, n = 4 at 2 and 3 weeks PI) of the BALB/c mice inoculated IP with 108 CFU/mouse of the correspondent mutant; the dashed lines indicate the detection limit (log10 5 CFU/spleen = 0.70) and normal splenic weight (0.1 g) in the BALB/c mice. (E) Cytokine profiles in blood sera and splenocytes supernatants from the same mice at selected intervals; sera collected at 2, 6, and 24 h PI (n = 5) were processed as pools, including two independent experiments for Rev1Δwzm, Rev1, and PBS groups; dotted lines represent PBS’s maximum value; blood sera and splenocytes supernatants collected at 1, 2, 3, and 4 weeks PI were processed individually for each necropsied group (mean ± SEM). Fisher’s LSD test; ***p ≤ 0.001, **p ≤ 0.01, *p ≤ 0.05 immune vs. non-immune sera for a given strain.