FIGURE 3.
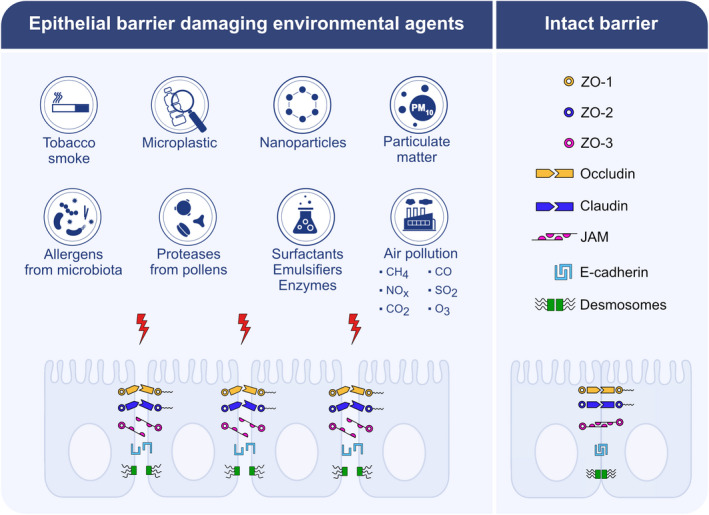
Epithelial barrier damaging agents from the environment. Allergens derived from bacteria, virus, and fungus; protease activity of allergens; surfactant, emulsifiers, and enzymes used as food additives; cigarette smoke, nanoparticles, particulate matter, and pollutant gases including nitric oxides, sulfur dioxide, carbon monoxide, carbondioxide, methane, ozone; microplastics irreversibly damage epithelial barriers by disrupting intercellular connections and anchoring of epithelial cells. Zonula occludens 1–3, occludin, claudins, junctional adhesion molecules, E‐cadherin and desmosomes are depicted as damaged epithelial molecules. CH4: methane, NOx: nitric oxides, CO2: carbondioxide, CO: carbon monoxide, SO2: sulfur dioxide, O3: ozone, ZO: Zonula occludens, JAM: junctional adhesion molecules
