FIGURE 4.
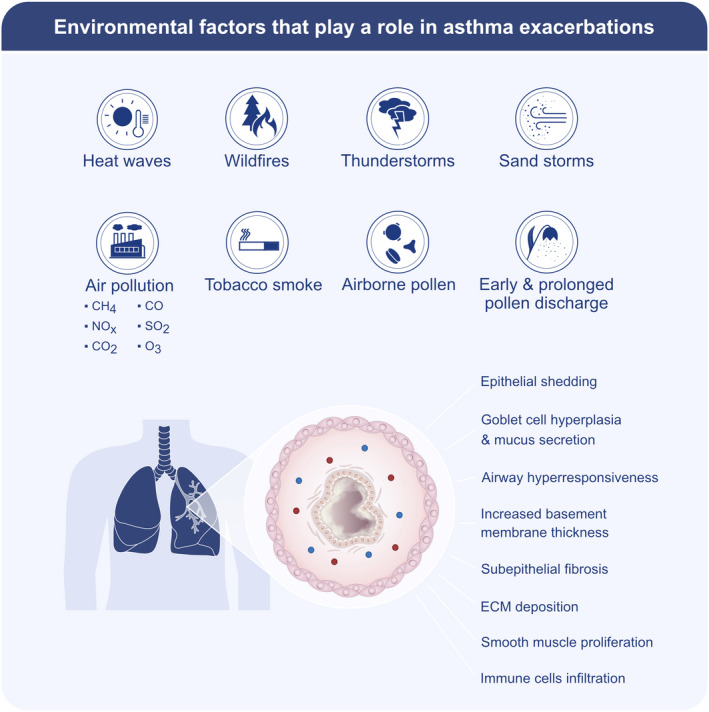
Environmental factors that play a role in asthma exacerbations. Air pollution with gases (NOx, SO2, O3, CO2, CO, CH4) and particulate pollutants (PM2.5 and PM10) emitted from industrial smog and wildfire smog, environmental tobacco smoke, heat waves, sandstorms, and airborne pollen cause asthma exacerbations. Moreover, extreme heat causes early and prolonged pollen discharge, and thunderstorms cause bioaerosols containing potentially allergenic small particles due to the rapid hit of water droplets to the ground. All of these factors may have a direct or indirect effect on epithelial shedding, goblet cell hyperplasia, airway hyperresponsiveness, increased basement thickness, subepithelial fibrosis, extracellular matrix (ECM) deposition, smooth muscle proliferation, and immune cell infiltration in the airways and exacerbate asthma
