Fig.6.
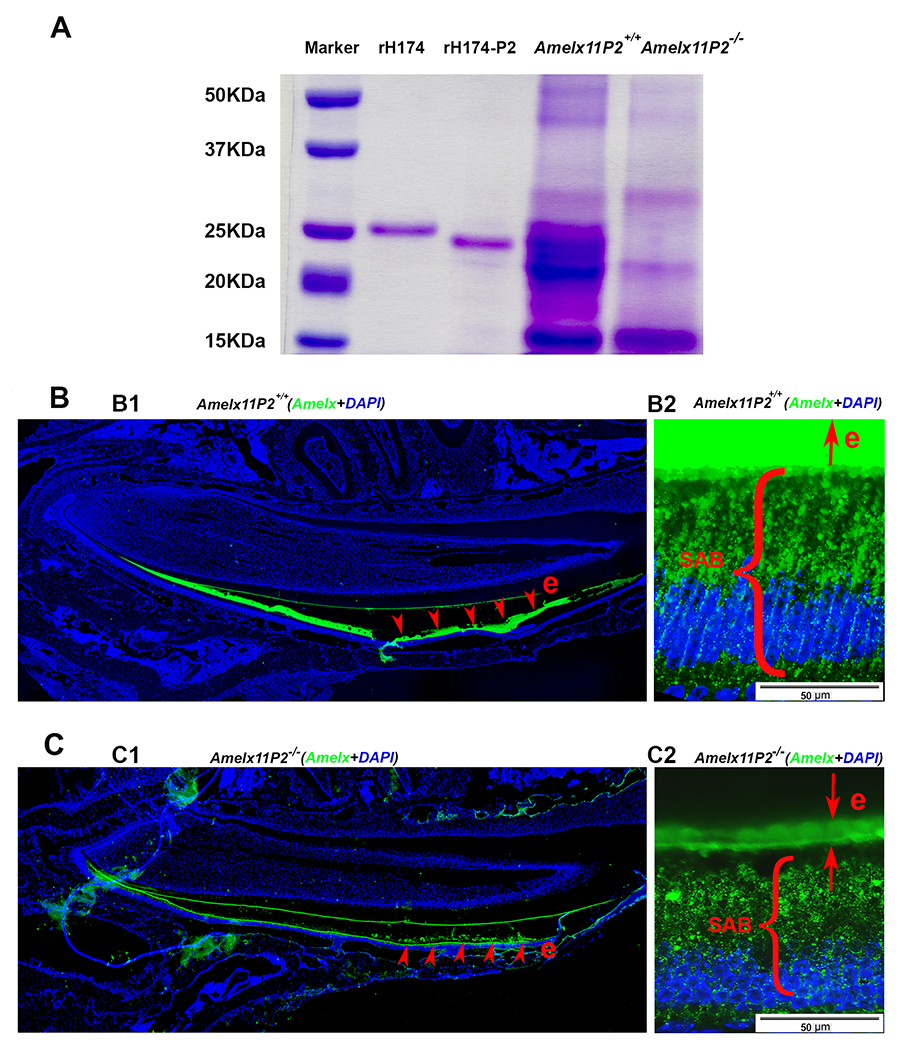
Assessment of effects of 11P2 deletion on the amelogenin proteins present in the developing enamel organ. A) SDS-PADG analysis shows that there was more protein content in Amelx11P2+/+ secretory stage enamel matrix as compared to Amelx11P−/− enamel matrix. Most of Amelx11P2+/+ matrix proteins migrated as proteins at size between 20-25 kDa. There was a heavy band about 22 kDa in Amelx11P2−/− enamel matrix. A band at about 14 kDa was revealed in both Amelx11P2+/+ and Amelx11P−/− enamel matrix. B1) Amelogenin immunostaining analysis on Amelx11P2+/+ mouse sagittal section shows that amelogenin signal (in green) was detected in the secretory and maturation stage of enamel matrix (e, pointed by the red arrows), but significantly reduced at the end of maturation stage. B2) Amelogenin immunostaining signal was very intense in Amelx11P2+/+ organic enamel matrix (e), and directionally distributed along the long-axis of secretory ameloblasts (SABs). C1) Amelogenin immunostaining analysis on Amelx11P2−/− mouse sagittal section shows that amelogenin signal (in green) was significantly reduced in the secretory and maturation stage of enamel matrix (e, pointed by the red arrows). C2) Amelogenin was immune localized in the thin Amelx11P−/− enamel matrix and in the cytosols in a disordered manner.
