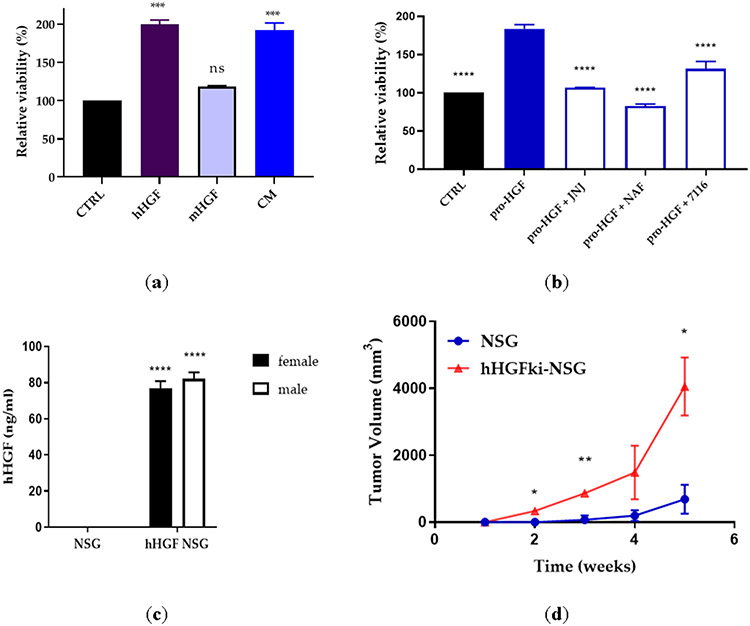
Figure 8. H596 cell and tumor growth is dependent on hHGF, but not mHGF.
(a) H596 lung cancer cells were incubated with recombinant hHGF (50 ng/ml), mHGF (50ng/ml), or fibroblast conditioned medium (CM). Cell viability was determined after 72h by CellTiterGlo. Statistical significance was calculated using one-way ANOVA and is shown compared to CTRL. (b) H596 lung cancer cells were incubated with recombinant pro-HGF (50 ng/ml) in the presence or absence of JNJ-38877605 (JNJ; 500 nM), nafamostat (NAF; 33.3 μM), or ZFH7116 (10 μM). Statistical significance was calculated using one-way ANOVA and is shown compared to cells stimulated with pro-HGF. (c) The serum concentration of hHGF in male and female NSG and hHGFki-NSG mice was assessed by hHGF ELISA. n=3 for NSG males and females and n=6 for hHGF NSG males and females. Statistical significance was calculated using 2way ANOVA and is shown compared to NSG animals. (d) Comparison of H596 lung cancer cell growth in NSG and hHGFki-NSG mice. Mice were injected subcutaneously with 0.5 million H596 cells. n=3 for each group. Statistical significance was calculated using 2way ANOVA. (a-d) *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001, ****P<0.0001.