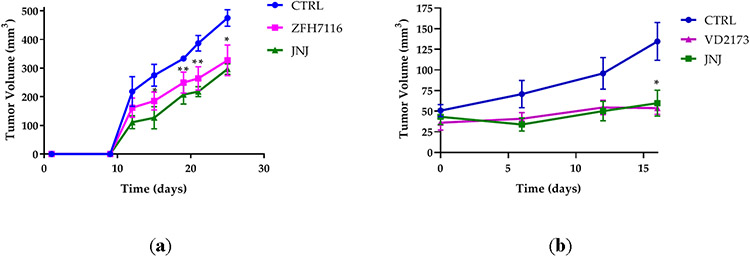
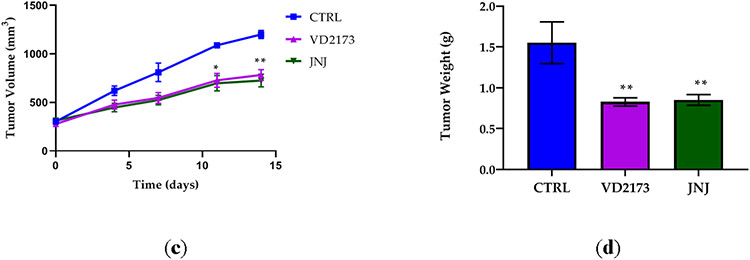
Figure 9. VD2173 and ZFH7116 block HGF-dependent tumor progression.
(a) H596 tumor growth in hHGF-KI NSG female mice injected with ten million H596 cells and treated with ZFH7116 (50 m/kg daily; IP) or JNJ-38877605 (40 mg/kg daily; PO) for 25 days. The treatment started immediately after tumor cell injection. n=3-5 for each group. (b) hHGF-KI NSG female mice were injected with 2 million H596 cells. When tumor volume reached ~ 40mm3, animals were divided into three groups and treated daily with control (IP and PO), VD2173 (20 mg/kg; IP), or JNJ-38877605 (40 mg/kg; PO) for 16 days. n=4-6 for each group. (c) hHGF-KI NSG male mice were injected with 0.5 million H596 cells. When tumor volume reached ~350mm3, animals were divided into three groups, and treated with VD2173 (20 mg/kg daily; IP) or JNJ-38877605 (40 mg/kg daily; PO) for 14 days. n=3-4 for each group. (d) Tumors in (c) were collected and weighed at the end of the experiment. n=3-4 for each group. Statistical analysis was performed using two- and one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) with Dunnett’s multiple comparison test and statistical significance is indicated for sHAI or JNJ-treated mice compared to control-treated mice (a-c) *P<0.05, **P<0.01