Figure 2.
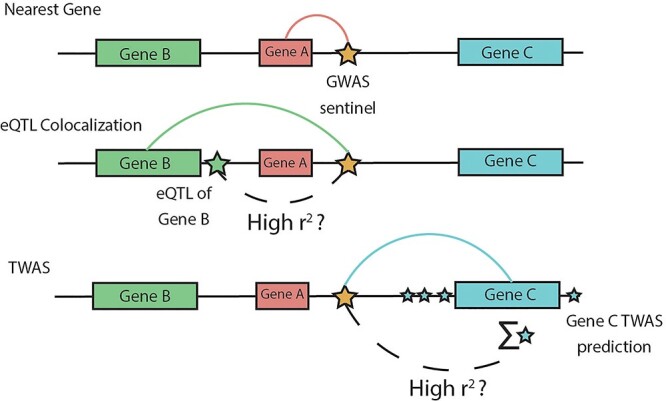
TWAS variant-to-gene approach. Comparison of our TWAS-based approach to variant-to-gene assignment with two commonly used approaches: distance-based and colocalization-based assignments. We consider the problem of assigning a GWAS variant (gold star) in a non-coding region to a target gene. The nearest gene approach assigns the variant to the closest gene at the locus (Gene A), but ignores epigenomic evidence at the locus. Colocalization-based approaches assign the variant to a target gene based on evidence that the GWAS signal is not distinct from an eQTL signal for a target gene (green star, Gene B). Our TWAS-based approach assesses the correlation between the GWAS variant and TWAS predicted gene expression which aggregates smaller effect cis-eQTLs for a gene (blue stars, Gene C). For presentation brevity, we use ‘high r2’ but the threshold to define high correlation can be lenient.
