Figure 2.
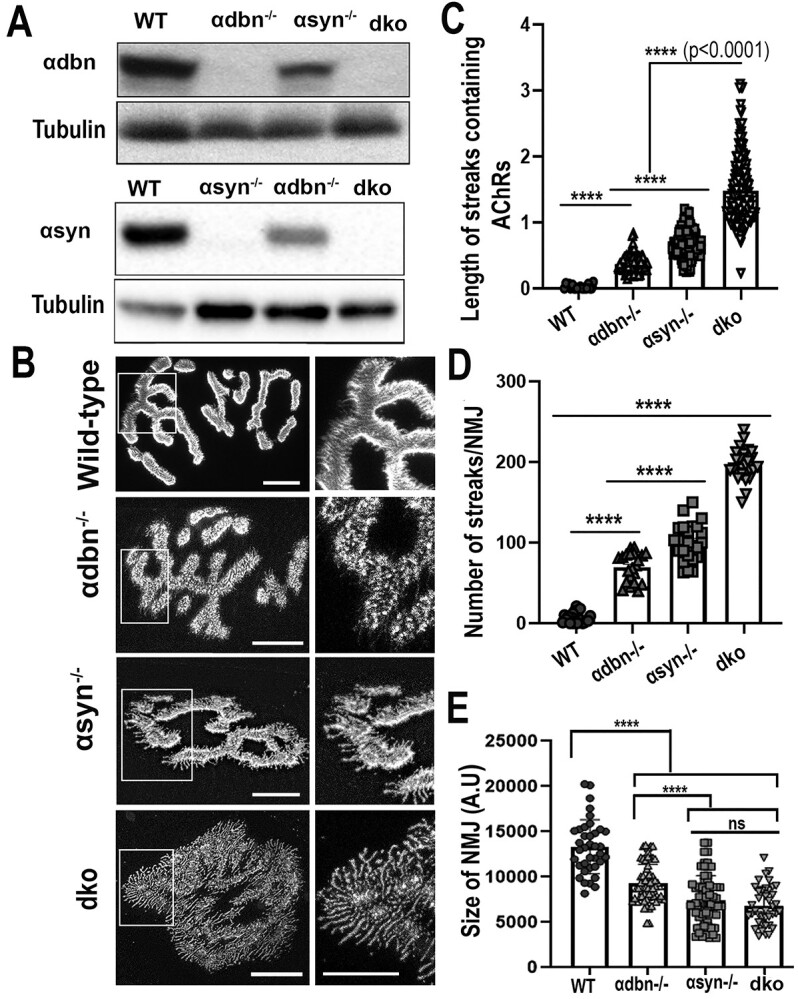
Characterization and analysis of the NMJs of double homozygote knock-out (α-dbn−/−, α-syn−/−) mice. (A) Western blots of skeletal muscle homogenates from dko confirming the absence of α-dbn and α-syn proteins. Tubulin was used as a loading control. (B) Sternomastoid muscles of young adult mice (2–3 month-old) from wild-type, α-dbn−/−, α-syn−/−, and dko (α-dbn−/−; α-syn−/−) were fixed and stained with α-BTX-AlexaFluor 488. Examples of representative images of NMJs stained with a fluorescent BTX from the above mice are shown. (C) Quantification of the length of membrane containing AChRs. Note that in NMJs from dko, the lines of AChRs extending beyond the undefined gutters were significantly longer than either α-syn or α-dbn mutant synapses. (D) Histogram showing the frequency of the abnormal AChR extensions beyond synaptic gutters. (E) Quantification of areas occupied by AChRs (synaptic size). Note that the synaptic size of single and double mutants was significantly reduced compared to wild-type, while there was no significant difference between α-syn−/− and dko genotypes. Scale bars: 10 μm.
