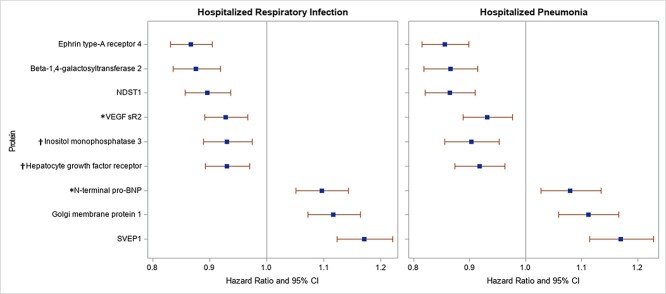
Figure 1.
Cox regression analysis of significant proteins and risks of incident hospitalized respiratory infection (n for events = 2570) and hospitalized pneumonia (n for events = 2087) among ARIC participants over median 20.7- and 21.5-year follow-ups, respectively. Model: the Cox proportional hazards regression model assessed associations of proteins (per SD) with risks of incident infection outcomes with adjustments for age, gender, race, field center, eGFR, cigarette smoking status, BMI, prevalent diabetes, alcohol drinking status, estimated ethanol intake (grams/week), total cholesterol, prevalent cardiovascular disease, and prevalent stroke. Protein values outside of 6 SDs from the mean were excluded for each protein, and Bonferroni correction stipulated a significance level of P ≤ 5.9 × 10−4.
*VEGF sR2 and N-terminal BNP were significantly associated with incident respiratory infection but did not reach the Bonferroni corrected significance threshold for the pneumonia outcome. Inositol monophosphatase 3 and hepatocyte growth factor receptor were significantly associated with incident pneumonia but did not reach the Bonferroni-corrected significance threshold for the respiratory infection outcome. VEGF sR2 = vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2.