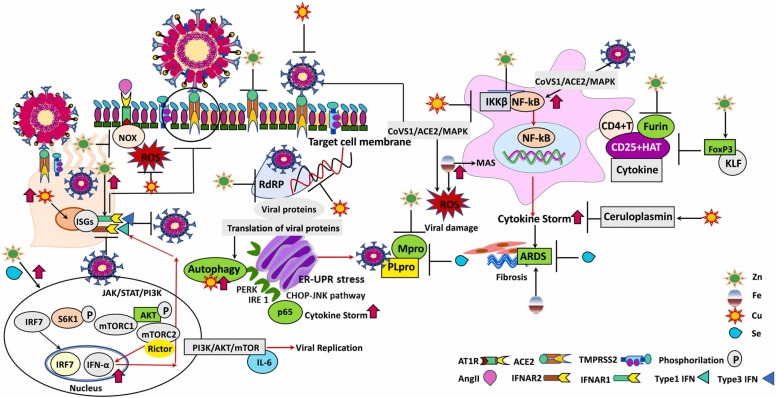
Fig. 1.
SARS-CoV-2 binds to ACE2 receptors on the respiratory epithelium and infiltrating macrophages, leads to activation of the inducible transcription factor, NF-κB. Subsequently, it induces “cytokine storm” and eventually provokes ARDS. Labile iron in the cell that promotes MAS is characterized by cytokine storm and contributes to the formation of ROS. In PI3K-Akt-mTOR pathway nuclear translocation of IRF7 leads to transcriptional activation of type I interferon (IFN) genes. The key component of mTORC2, Rictor regulates IFN-α production. The produced IFN-α binds to IFN-α receptors (IFNAR1-IFNAR2) and provides immune protection against SARS-CoV-2. Zn, Cu and Se target multiple pathways to hamper the functional and structural consequences of inflammatory response caused by SARS-CoV-2 and inactivates the viral genomes of SARS-CoV-2 and exhibits irreversible effects on virus morphology. Thus, envelope disintegration and dispersal of spike protein occurs. Zinc and Se on the one hand suppress the life cycle of SARS-CoV-2 by inhibiting Mpro and PLpro of SARS-CoV-2, on the other hand strengthen the immune defense and counteract to the complications of SARS-CoV-2 infection (Abbreviations. ACE2: the cell receptor angiotensin-converting enzyme II; AKT: protein kinase B; AngII: angiotensin II; ARDS: acute respiratory distress syndrome; AT1R: angiotensin II receptor type 1; CHOP: CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein (C/EBP)-homologous protein; CoVS1: SARS-CoV-2 Spike protein; Cu: copper; ER: endoplasmic reticulum; Fe: iron; FoxP3: the transcription factor forkhead box P3; HAT: CD25 + hyperactivated T-cells; IFNAR: IFN α receptor; IFNα: (type-1 interferon) interferon alpha; IKKβ: IκB kinase β; IL-6: interleukin-6; IRE1: inositol-requiring enzyme 1; IRF7: interferon regulatory factor 7; ISG: interferon-stimulated gene; JAK: janus kinase; JNK: c-Jun N-terminal kinase; KLF: Krüppel-like transcription factor; MAPK: p38-mitogen-activated protein kinases; MAS: macrophage activation syndrome; Mpro: a key enzyme of SARS-CoV-2 and has a pivotal role in mediating viral replication and transcription; mTORC1: mammalian target of rapamycin complex 1; mTORC2: mammalian target of rapamycin complex 2; NFκB: nuclear factor-κB; NOX: nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH) oxidase; p: phosphorylation; PERK: protein kinase r-like endoplasmic reticulum kinase; PI3K: phosphoinositide 3-kinase; PLpro: papain-like protease of SARS-CoV-2; RdRp: RNA dependent RNA polymerase; Rictor: The rictor-mTOR complex directly phosphorylated AKT; ROS: reactive oxygen species; S6K1: s6 kinase 1; Se: selenium; STAT: signal transducers and activators of transcription; TMPRSS2: the serine protease of SARS-CoV receptor ACE2 in S protein priming for entry to target cell; UPR: unfolded protein response; Zn: zinc).