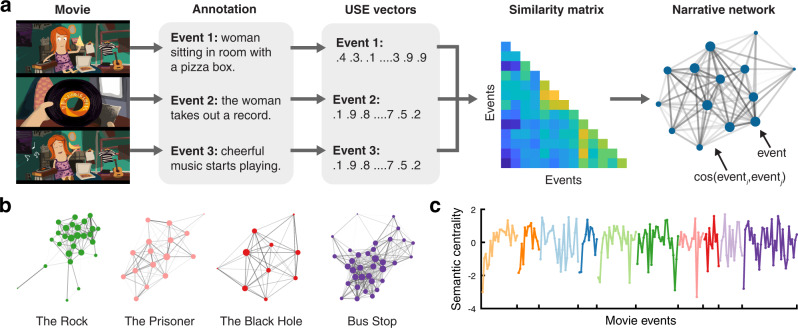
Fig. 1. Semantic narrative networks.
a To create semantic narrative networks, each movie was split into events, and independent annotators provided text descriptions of the events. The text descriptions were transformed into sentence embedding vectors using Google’s Universal Sentence Encoder (USE)25. Semantic similarity between events was computed as the cosine similarity between the USE vectors. A semantic narrative network was defined as a network whose nodes are movie events and the edge weights are the semantic similarity between the events. b Semantic narrative networks of four example movies used in the fMRI experiment. Edge weights were thresholded at cosine similarity = .6 for visualization purposes. Node size is proportional to centrality computed from unthresholded networks. Edge thickness is proportional to edge weights. c Semantic centrality (normalized degree) for individual movie events of the 10 movies used in the fMRI experiment. Different colors denote different movies. Source data are provided as a Source Data file. For the semantic similarity matrices and narrative networks of all 10 movies, see Supplementary Fig. 3. Movie scene images in a were created by the author H. L. using Adobe Illustrator (adobe.com).