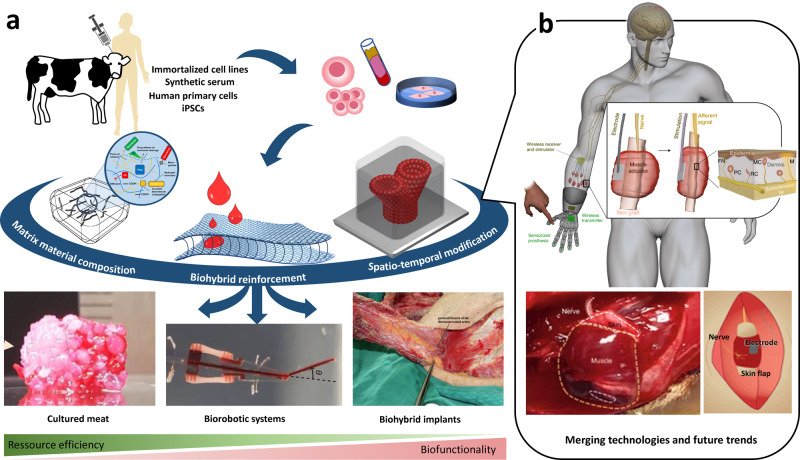
Fig. 1. Biofabrication of muscle tissue and merging the expertise of the different fields of applications.
Biofabrication of muscle tissue enables multiple applications (a) ranging from cultured meat155 (assembly of fibrous muscle, fat, and vascular tissues to cultured steak by Kang et al (CC BY 4.0)), over biorobotic systems (from ref. 2. Reprinted with permission from AAAS.) to biohybrid implants3 (the pectoral branch of the thoracoacromial artery was identified beneath the pectoralis major by Liu et al (CC BY 4.0)). This review provides a comprehensive overview on the most important cellular and material-specific requirements as well as dedicated biofabrication strategies(adapted from refs. 22,148 (Schematic illustration of the concept, experimental procedure, goal, and outlook of the study by Schäfer et al. (CC BY 4.0))) for each of the three fields of application. While biofabrication of cultured meat, biorobotic systems, and bioartificial muscle implants has mostly been studied in isolation so far, the technological fusion will unleash unexpected innovations and determine future trends. The recently published combination of biorobotic systems and biohybrid implants is a path-breaking pointer to what lies ahead (b, adapted from Srinivasan and co-workers153 (reprinted with permission from Springer Nature Limited: Nature Biomedical Engineering, A cutaneous mechanoneural interface for neuroprosthetic feedback, Srinivasan et al., Copyright 2021).