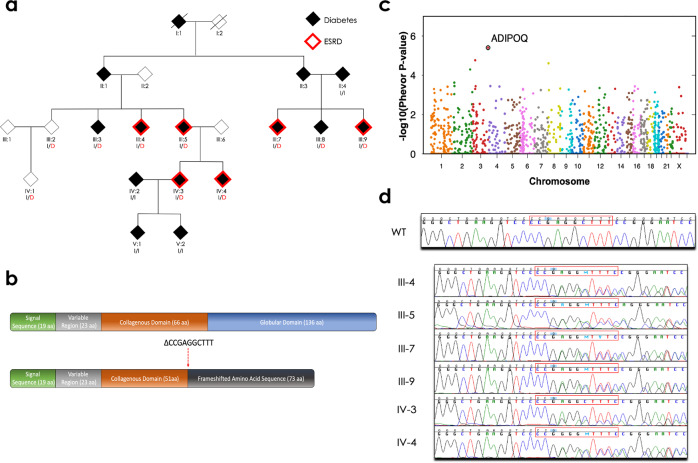
Fig. 1. Pedigree of the family enriched for diabetes and end-stage renal disease and identification of the ADIPOQ mutation.
a The family pedigree, status of diabetes (shaded) and end-stage renal disease (ESRD; red outline), and the ADIPOQ mutation (p.Gly93GlufsTer73). Carriers of the wild-type ADIPOQ insertion (I) or mutated ADIPOQ deletion (D; red) are indicated. b The structure of the wild-type (top) and mutant (bottom) adiponectin protein. Wild-type adiponectin monomers consist of a 244 amino acid protein composed of four domains; an N-terminal signal sequence (19 amino acids), a variable region (23 amino acids), a collagenous domain (66 amino acids), and a C-terminal globular domain (136 amino acids). The 10-nucleotide deletion (CCCGAGGCTTT→C, indicated as ∆CCGAGGCTTT) at amino acid 93 creates a frameshift that truncates the adiponectin protein and generates a novel peptide that terminates 73 amino acids after this deletion. c The PHEVOR plot using Human Phenotype Ontology (HPO) terms and connections to Gene Ontology terms to prioritize potentially damaging alleles, using terms for a) kidney disease: HP:0000077 (Abnormality of the kidney), HP:0000112 (Nephropathy), and HP:0003774 (Stage 5 chronic kidney disease), and b) diabetes: HP:0000819 (Diabetes) and HP:0005978 (Type 2 diabetes mellitus) and a combination of the pVAAST p values and PHEVOR scores. PHEVOR scores (y-axis) for each gene (dot) are plotted across the genome (x-axis, chromosomes 1-Y). d The chromatogram from Sanger sequencing of a non-carrier from the family (WT) and the 6 carriers identified through whole-genome sequencing and pVAAST/PHEVOR analysis.