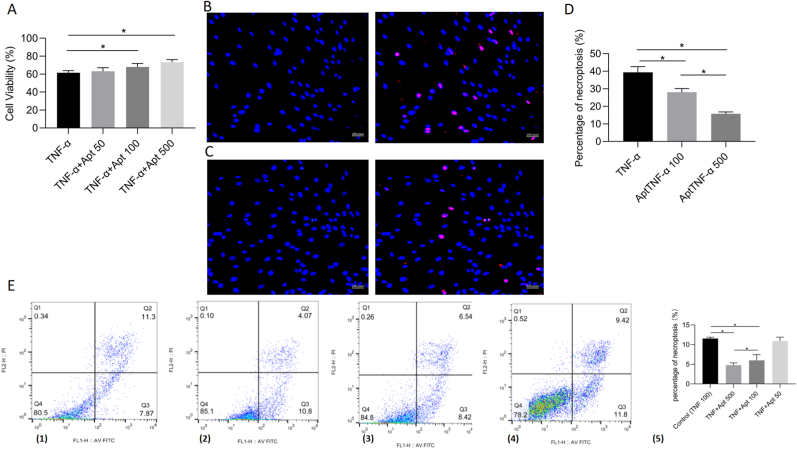
Figure 4.
AptTNF-α attenuated TNF-α cytotoxicity in a dose-dependent manner. A, Cell Counting Kit-8 results of cell viability after incubation with TNF-α and AptTNF-α for 24 h (n = 3, each group consisted of three repeated wells for analysis). B, the TUNEL staining results of the 100 ng/ml TNF-α + 100 nM AptTNF-α group. C, the TUNEL staining results of the 100 ng/ml TNF-α + 500 nM AptTNF-α group. D, the percentage of cell necroptosis from the TUNEL staining in 100 ng/ml TNF-α, 100 ng/ml TNF-α + 100 nM AptTNF-α, 100 ng/ml TNF-α + 500 nM AptTNF-α group (n = 3, each group consisted of three repeated wells for analysis). E, (1)–(4) the BMECs were stained with the Annexin V-FITC/propidium iodide (PI) in the 100 ng/ml TNF-α, 100 ng/ml TNF-α + 500 nM AptTNF-α, 100 ng/ml TNF-α + 100 nM AptTNF-α and 100 ng/ml TNF-α + 50 nM AptTNF-α, respectively. The cells in the Q2(UR) and Q1(UL) stand for the percentage of necroptosis. (5) Quantitative data of the Annexin V-FITC/PI results in these four groups (n = 3, each group was repeated three times in six-well plate for analysis). ∗p < 0.05. BMEC, bone microvascular endothelial cell. AptTNF-α, TNF-α aptamer.