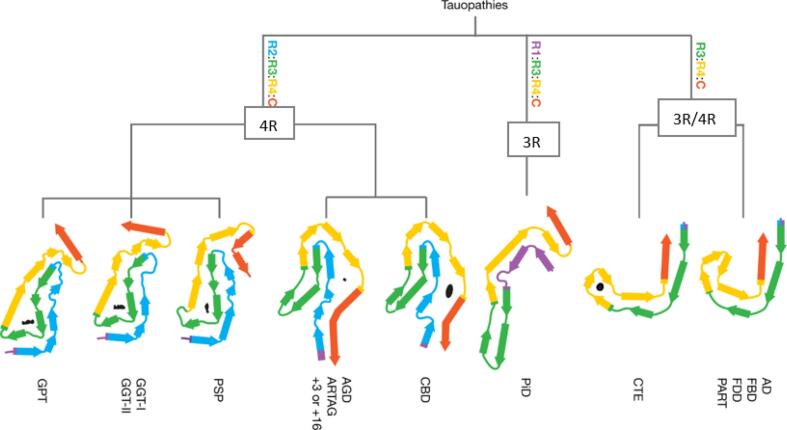
Fig. 3.
Structural classification of tauopathies based on cryogenic electron microscopy (cryo-EM). Tau residues are depicted by colouration and listed from R1-R4. Tau filament composition is classified according to 1) composition by isoforms and 2) core layer structure. Among the 3R/4R tauopathies, the CTE tau fibril is distinct from AD, FBD, FDD, and PART fibrils. Similarly, the 4R tauopathies are divided into two classes with either three-layered core regions (PSP, GPT, and GGT) or four-layered core regions (CBD, ARTAG, and AGD). AD = Alzheimer’s disease, FBD = familial British dementia, FDD = familial Danish dementia, PART = primary age-related tauopathy, CTE = chronic traumatic encephalopathy, PiD = Pick’s disease, CBD = corticobasal degeneration, AGD = argyrophilic grain disease, ARTAG = ageing-related tau astrogliopathy, PSP = progressive supranuclear palsy, GGT = globular glial tauopathy, GPT = GGT-PSP-tau. Figure is modified from Shi Y, Zhang W, Yang Y, Murzin AG, Falcon B, Kotecha A, van Beers M, Tarutani A, Kametani F, Garringer HJ, Vidal R, Hallinan GI, Lashley T, Saito Y, Murayama S, Yoshida M, Tanaka H, Kakita A, Ikeuchi T, Robinson AC, Mann DMA, Kovacs GG, Revesz T, Ghetti B, Hasegawa M, Goedert M, Scheres SHW. Structure-based classification of tauopathies. Nature. 2021 Oct;598(7880):359–363. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-021-03911-7. Epub 2021 Sep 29. PMID: 34588692; PMCID: PMC7611841.