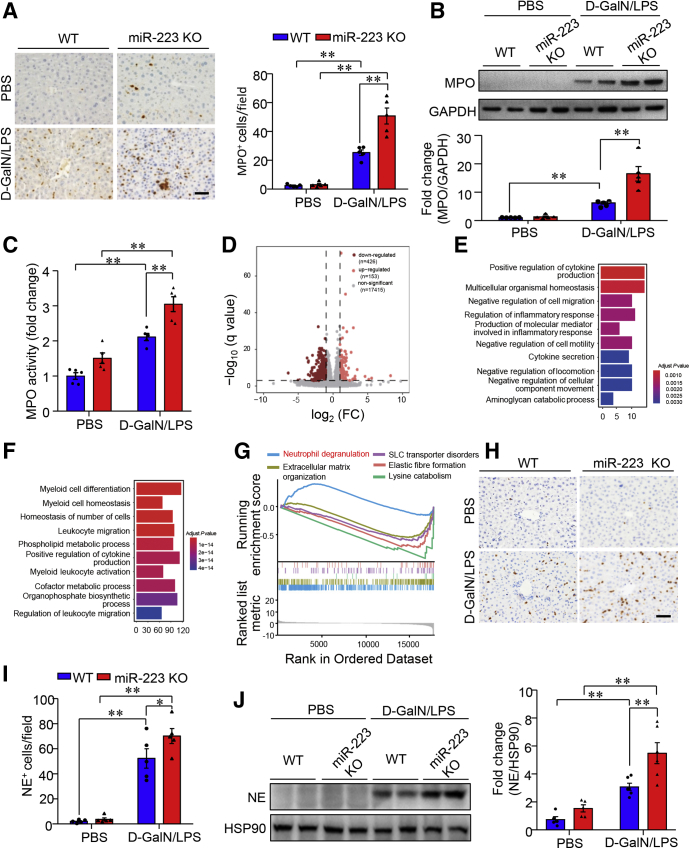
Figure 7.
Deletion of miR-223 augments hepatic recruitment of neutrophils and NE contents in mouse liver with ALF. Ten-week-old male miR-223 KO mice and WT controls were subjected to intraperitoneal injection of D-GalN/LPS to induce ALF (D-GalN 0.75 mg g-1 body weight, LPS 2.5 μg g-1 body weight). (A) Neutrophil infiltration in the liver was determined by immunohistochemistry of MPO (left, representative images) and semiquantification of MPO+ cells/per 40× microscopic field (right). Scale bar: 10 μm. The levels of MPO (B) protein contents and (C) enzymatic activities in liver lysates. (D) Volcano plot of RNA-seq data using bone marrow cells from miR-223 KO and WT control mice. n = 4 per group. Gene Ontology enrichment analyses of the target genes with marked (E) up-regulation and (F) down-regulation in miR-223 KO mice relative to WT controls. (G) Top 5 ranked Reactome pathways enriched in miR-223 KO bone marrow cells vs WT controls. (H–J) The abundance of NE in the liver from miR-223 KO and WT mice treated with either D-GalN/LPS or PBS were measured by (H) immunohistochemistry (representative images with original magnification, 400×; scale bar: 10 μm) with (I) semiquantification of NE+ cells per 40× microscopic field, and (J) immunoblotting analysis. Data are expressed as means ± SEM. n = 5 in functional studies. ∗P < .05, ∗∗P < .01. HSP90 heat shock protein 90.