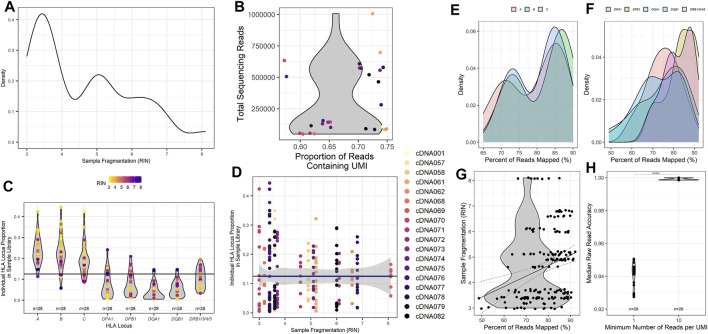
FIGURE 2.
Metrics for HLA typing using unique molecular identifier-tagged RNA demonstrates that as fragmentation decreases, more reads are obtained for sequencing, and a greater proportion of reads can be mapped to HLA loci of interest. (A) Calculated RNA integrity numbers for each patient sample with their measured band density post isolation and clean-up. (B) Sample sequencing reads acquired and the proportion of the reads that contain recognized UMI barcodes. (C) The proportion of reads per classical HLA locus per patient sample as counted using UMI reads. (D) The proportion of reads for each HLA locus compared to the calculated RNA integrity number for each patient sample. (E) The percentage of cDNA reads obtained that could be mapped to the HLA loci obtained during sequencing and their respective calculated sample RNA integrity numbers. (F) Read accuracy calculated for the minimum number of UMIs required for each HLA locus and sample after concatenation of cDNA reads to consensus sequences. The percentage of (G) class I and (H) class II HLA-specific reads mapped compared to input isolated RNA measured band density (****p value <0.001).