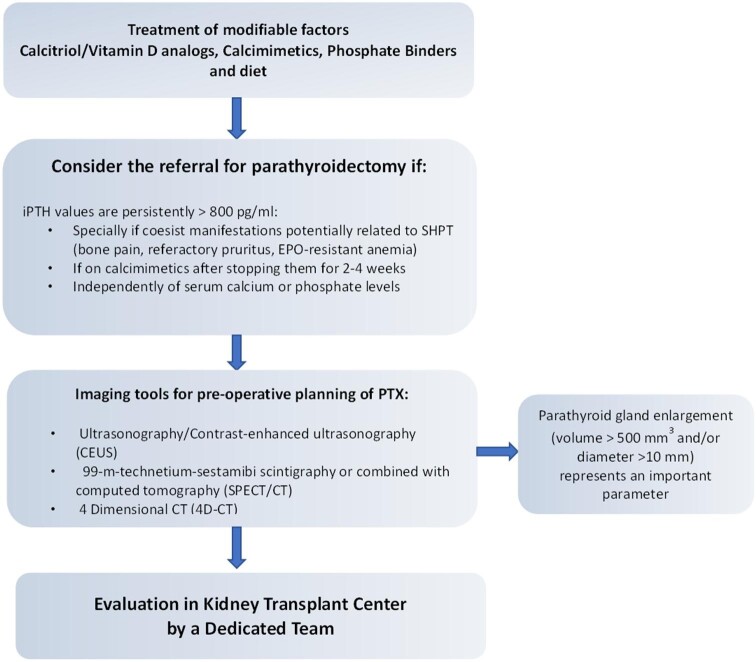
FIGURE 7:
Roadmap to parathyroidectomy for kidney failure patients with SHPT candidates to KT. The first step to reduce the risk of persistent HPT in KT candidates is the correction of modifiable factors: hypocalcemia, hyperphosphatemia, hyperparathyroidism (PTH target values 2–9 times the upper limit of normal in dialysis patients). If PTH levels are >800 pg/mL with or without hypercalcemia and/or hyperphosphatemia and symptoms or complications coexist related to SPHT, referral for parathyroidectomy should be considered. Imaging is necessary for preoperative parathyroidectomy planning, aimed to localize and define the size of parathyroid glands. Enlarged parathyroid glands (volume >500 mm3 and/or diameter >10 mm) represent a further parameter, in addition to high PTH levels, in the decision-making regarding parathyroidectomy. In our centers, a multidisciplinary team (nephrologists, otolaryngologists, radiologists) decides on the indication of parathyroidectomy based on preoperative findings. In all cases, CEUS is performed a few days before surgery by an expert and dedicated sonographer in the presence of the nephrologist and surgeon to verify helpful landmarks (skin, vascular axis, trachea, esophagus, upper and lower thyroid poles) for surgery.
EPO, erythropoietin; 4D-CT, 4-dimensional computed tomography.