Figure 1:
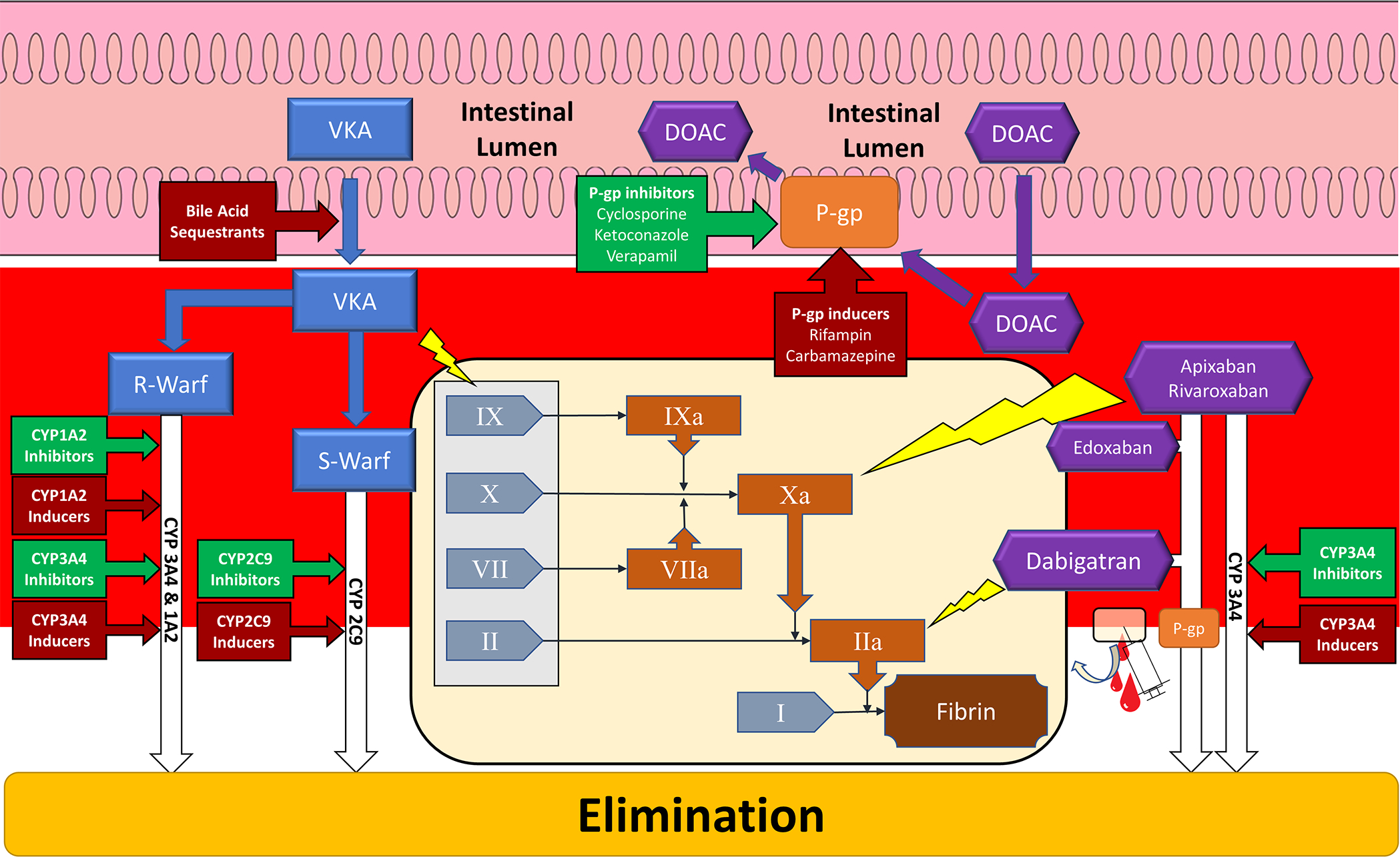
Schematic of major vitamin K antagonist and direct oral anticoagulant sites of drug interactions. Tan panel depicts simplified coagulation cascade and yellow lightning bolts indicate sites of inhibition by anticoagulants (blue rectangles – vitamin K antagonist; purple hexagons – direct oral anticoagulant). Gray rectangle encompass coagulation factors affected by vitamin K antagonism. Red arrowed boxes indicate interactions that inhibit anticoagulation. Green arrowed boxes indicate interactions that potentiate anticoagulation. CYP – Cytochrome P-450; DOAC – Direct oral anticoagulant; R-Warf – R-warfarin; S-Warf – S-warfarin; P-gp – P-glycoprotein; VKA – Vitamin K Antagonist; I – Fibrinogen; II – Prothrombin; IIa – Thrombin; VII – Factor 7; VIIa – Activated Factor 7; X – Factor 10; Xa – Activated Factor 10; IX – Factor 9; IXa – Activated Factor 9
