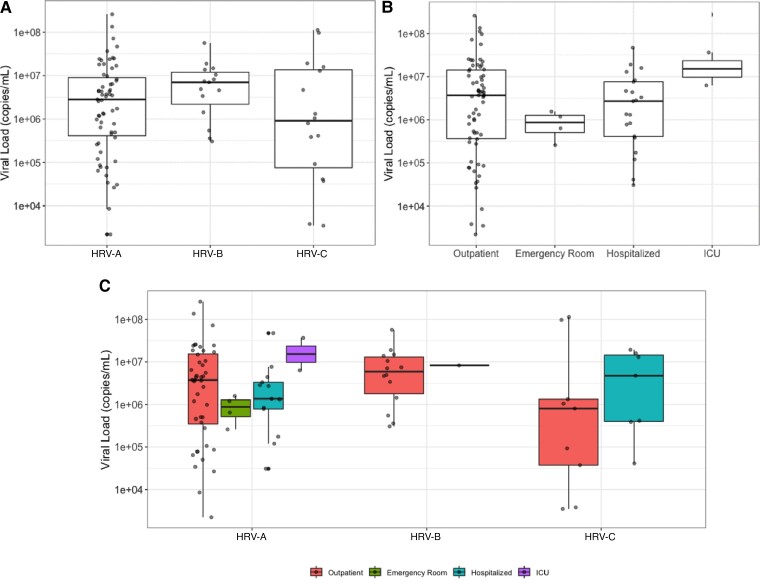
Figure 2.
Viral load (copies/mL) by human rhinovirus (HRV) type and hospitalization status at baseline. No statistically significant differences associated with HRV type (P = .243) (A) or hospitalization status (P = .318) (B). P values are from a Kruskal-Wallis test for comparison between groups. Abbreviations: HRV, human rhinovirus; ICU, intensive care unit.