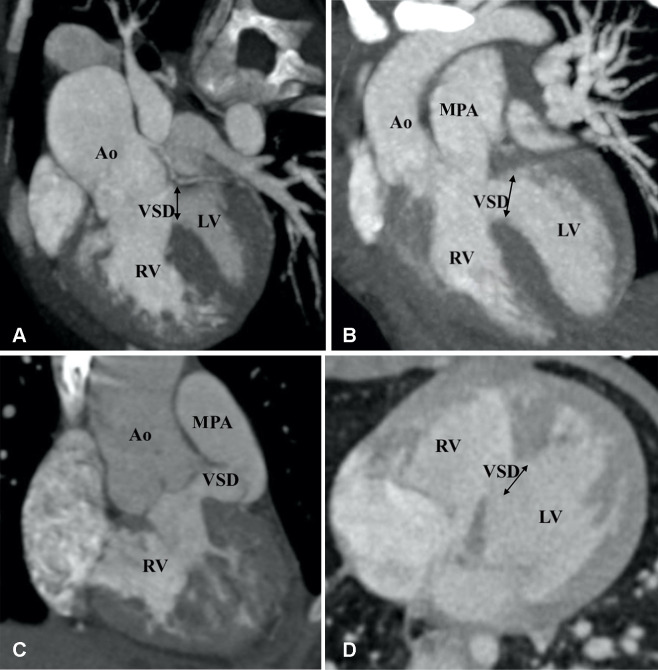
Figure 13:
Types of ventricular septal defects (VSDs). (A) Subaortic VSD (double arrow) in a 1-year-old boy with double-outlet right ventricle (DORV). Reformatted coronal maximum intensity projection (MIP) CT image shows greater than 50% aortic overriding. The pulmonary valve and MPA were severely stenotic (not shown). (B) Subpulmonic VSD (double arrow) in a 2-year-old boy with DORV. Reformatted coronal MIP CT image shows the origin of both great vessels from the RV. (C) Doubly committed VSD in a 2-year-old girl with DORV. Reformatted coronal MIP CT image shows the origin of both great vessels from the RV. VSD is closely related to both the semilunar valves (doubly committed). (D) Remote VSD (double arrow) in an infant with DORV. Axial MIP CT image shows remote intramuscular VSD. Ao = aorta, LV = left ventricle, MPA = main pulmonary artery, RV = right ventricle.