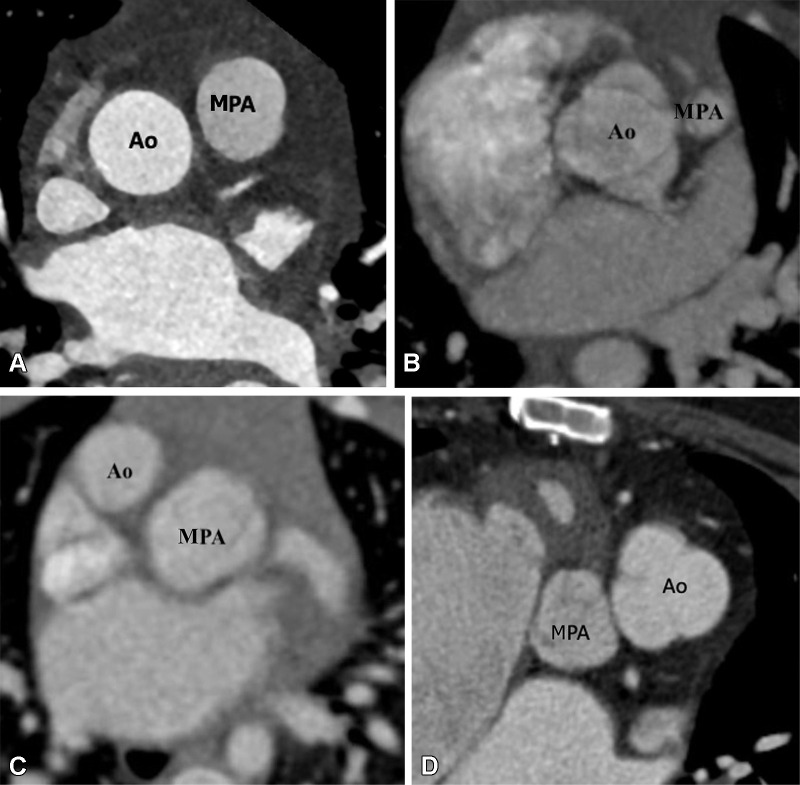
Figure 14:
Great vessels relationship. (A) Normal great vessels relationship in a 25-year-old healthy man. Axial contrast-enhanced CT image shows the ascending aorta is in a position posterior and to the right of the pulmonary artery. (B) Normal relationship in a 2-year-old boy with TOF-type DORV. Axial maximum intensity projection (MIP) CT image shows the ascending aorta in a position posterior and to the right of the pulmonary artery. Pulmonary stenosis is observed, which is a common feature of TOF-type DORV. (C) Dextrotransposition in a 1.5-year-old girl with TGA-type DORV. Axial MIP CT image shows the ascending aorta in a position anterior and to the right of the MPA. (D) Levotransposition in a 2-year-old girl with TGA-type DORV. Axial MIP CT image shows the ascending aorta in a position anterior and to the left of the pulmonary artery. Ao = aorta, DORV = double-outlet right ventricle, MPA = main pulmonary artery, TGA = transposition of the great arteries, TOF = tetralogy of Fallot.