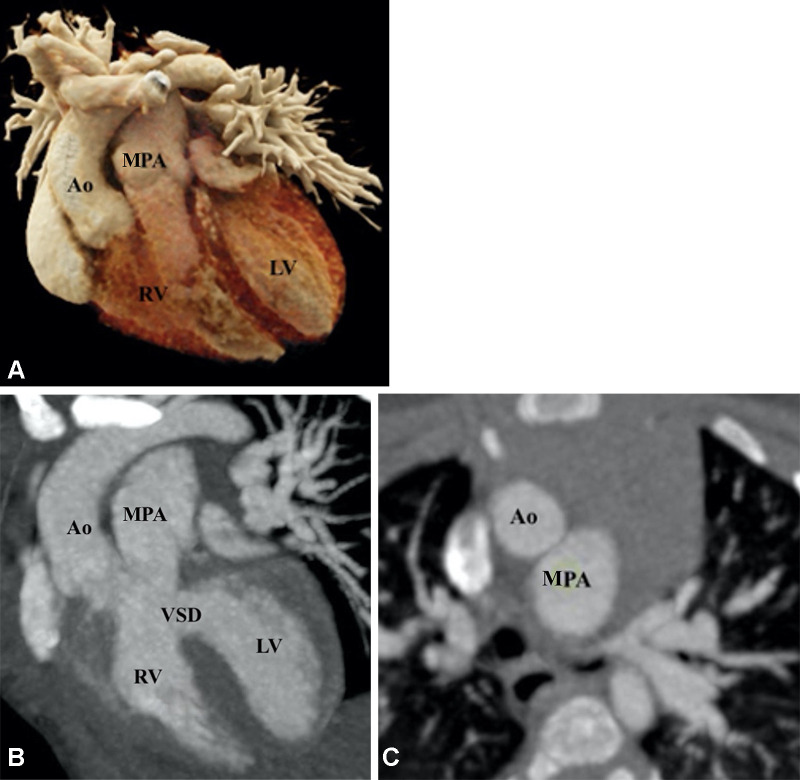
Figure 16:
Preoperative appearance of TGA-type DORV in a 2-month-old female infant. (A) Cinematic rendering technique image shows both the great arteries arising from the right ventricle. Both the great vessel trunks run parallel to each other, with the aorta on the right side. (B) Coronal reformatted maximum intensity projection (MIP) CT image shows a subpulmonic VSD. (C) Axial MIP CT image shows the great vessels relationship. The aorta is seen anterior and to the right of the MPA, suggesting dextrotransposition (D-TGA type) relationship. Ao = aorta, DORV = double-outlet right ventricle, LV = left ventricle, MPA = main pulmonary artery, RV = right ventricle, TGA = transposition of the great arteries, VSD = ventricular septal defect.