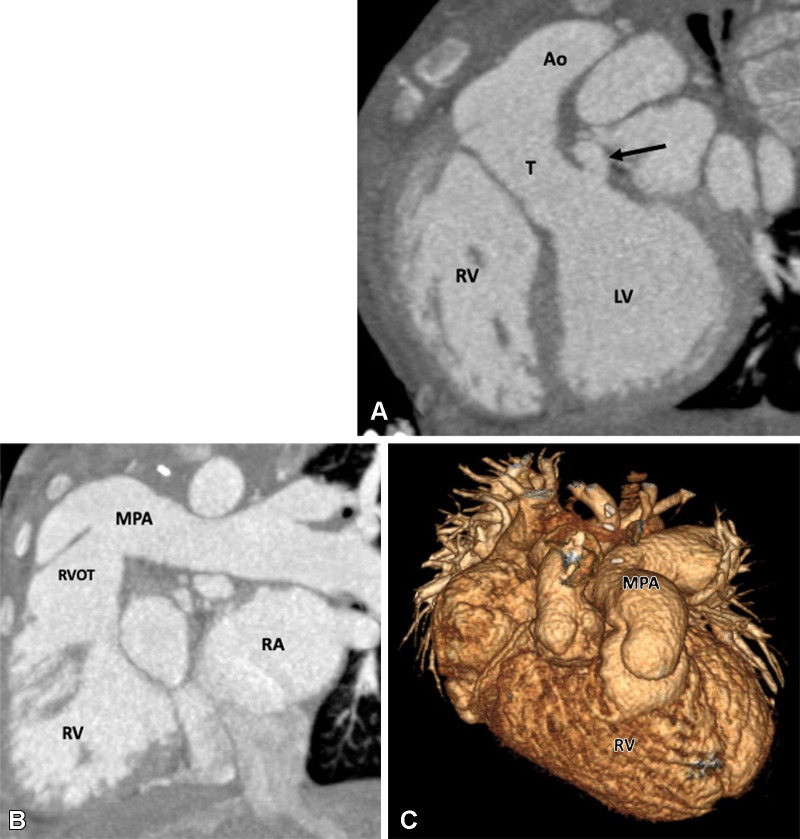
Figure 24:
Postoperative appearance after réparation à l’etage ventriculaire (REV procedure) for treatment of dextrotransposition of the great arteries, ventricular septal defect, and pulmonary stenosis in a 26-year-old man. (A) Sagittal oblique maximum intensity projection (MIP) CT image shows a small pseudoaneurysm (black arrow) arising from the LV outflow tract. (B) Sagittal oblique MIP CT image shows mildly dilated RV and RVOT. (C) Volume-rendered image shows direct implantation of the MPA on the RV lying anterior to the aorta. The REV procedure is similar to Rastelli repair, except the pulmonary artery is directly connected with the RV, avoiding the RV-MPA conduit. Ao = aorta, LV = left ventricle, MPA = main pulmonary artery, RA = right atrium, RV = right ventricle, RVOT = right ventricular outflow tract, T = tunnel.