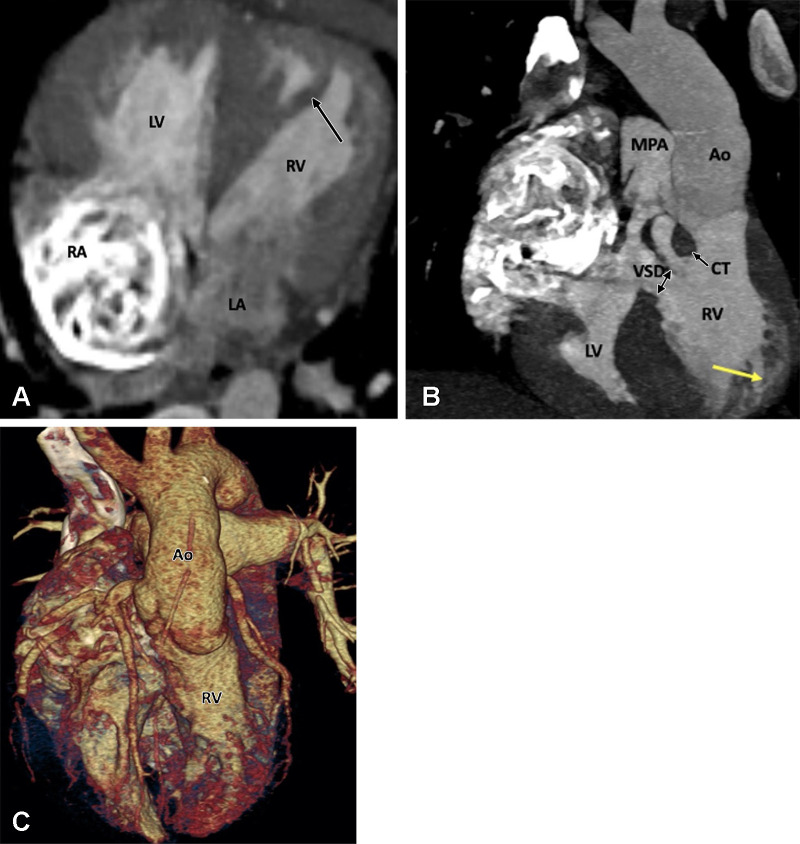
Figure 27:
Preoperative appearance of congenitally corrected transposition of the great arteries in a 25-year-old woman. (A) Axial oblique maximum intensity projection (MIP) CT image shows atrioventricular discordance. The RV is identified by the moderator band (black arrow). (B) Coronal oblique MIP CT image shows ventriculoarterial discordance. The aorta arises from the left-sided RV, and the pulmonary artery arises from the right-sided LV. The RV is identified by the trabeculated wall (yellow arrow). A thick conal tissue (black arrow) is seen in the subpulmonic region. In the primitive ventricle, it is present in both the subpulmonic and subaortic regions. During transfer of the aorta to the LV, the subaortic component gets resorbed and is represented by fibrous continuity between the aortic and mitral valve leaflets. The subpulmonary component, however, persists and separates the pulmonary and tricuspid valve. A VSD is also seen (double arrow). (C) Volume-rendered image further confirms the levotransposition of the aorta, which is located leftward and anterior to the pulmonary trunk. Ao = aorta, CT = conal tissue, LA = left atrium, LV = left ventricle, MPA = main pulmonary artery, RA = right atrium, RV = right ventricle, VSD = ventricular septal defect.