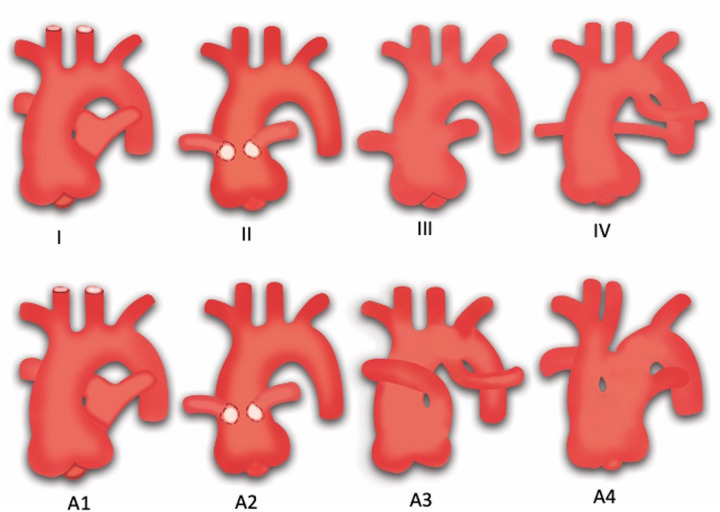
Figure 29:
Diagram shows two commonly used classification systems for truncus arteriosus. Top row represents the Collett and Edwards system. Type I truncus arteriosus is characterized by origin of the main pulmonary trunk from the truncus, which further divides into the right and left pulmonary arteries; type II is characterized by the separate origin of the right and left pulmonary arteries from the posterior aspect of the truncus; type III is characterized by the separate origin of the right and left pulmonary arteries from the lateral aspect of the truncus; and type IV represents pseudotruncus (pulmonary atresia with a ventricular septal defect). Bottom row represents the Van Praagh system. Types A1 and A2 are equivalent to the Collett and Edwards types I and II, respectively; type A3 is characterized by atresia of the left or right pulmonary artery, with collateral flow to the ipsilateral lung; and type A4 is characterized by the presence of an associated interrupted aortic arch. (Adapted, with permission, from references 131 and 132.)