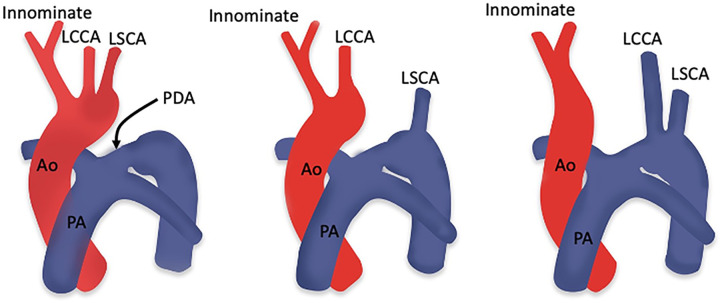
Figure 32:
Diagrams showing the three types of interrupted aortic arch. Type A (left) is characterized by aortic arch interruption distal to the left subclavian artery origin; type B (middle) is characterized by aortic arch interruption between the origins of the left common carotid artery and left subclavian artery; and type C (right) is characterized by aortic arch interruption between the origins of the innominate and left common carotid arteries. Ao = aorta, LCCA = left common carotid artery, LSCA = left subclavian artery, PA = pulmonary artery, PDA = patent ductus arteriosus. (Reprinted, with permission, from reference 124.)